If you're a small business registered under the GST Composition Scheme, GSTR-4 is the annual return you must file. It helps the government track your sales, purchases, and taxes paid during the year. Filing GSTR-4 on time is important as it keeps your business compliant with GST rules, helps you avoid penalties, and ensures smooth GST operations.
If you’re filing for the first time, this guide will help you handle GSTR-4 with confidence.
What is GSTR-4?
GSTR-4 is an annual return that taxpayers who have opted for the GST Composition Scheme must file. Unlike regular taxpayers who file monthly or quarterly returns, composition dealers are required to file just one return for the entire financial year using Form GSTR-4.
This return provides a detailed overview of your total sales, purchases, taxes paid, and any advances received during the year. It allows the government to monitor compliance with GST regulations while keeping the process simple and less time-consuming for small businesses.
Under the GST composition scheme, taxpayers will be required to file one only return in every three months (quarter) rather than multiple returns in every month as is the case for a regular dealer.
However, not all businesses will be eligible to register under the GST composition scheme - only those business entities, for whom the annual turnover is below INR 1.5 Crore and who also fulfil other specified criteria can be entitled to register under the Composition Scheme.
One of the key points to be noted here is, that dealers under the composition scheme will be required to pay taxes at fixed rates, without availing input tax credit facility.
Who should do GSTR - 4 filing?
Any taxpayer opting for the Composition Scheme is required to do GSTR-4 filing, except for:
- Non-resident Taxable Person
- Taxpayers liable to collect TCS
- Input Service Distributors
- Taxpayers liable to deduct TDS
- Compounding taxable person
- Suppliers of OIDAR (Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval)
Why is GSTR-4 important?
Even though composition dealers have fewer compliance obligations compared to regular taxpayers, filing GSTR-4 is still mandatory. It helps:
- Keep your business records in line with GST laws
- Avoid penalties and notices from the GST department
- Show transparency and accountability in your business operations
GSTR-4 is your way of telling the government: "Here's what I earned, here’s what I paid, and I’m doing things the right way."
GSTR-4 filing format
The updated annual form for GSTR-4 filing is made up of nine sections:
Table 1-3: Basic details
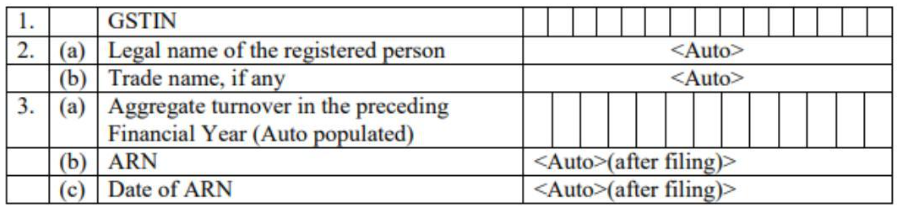
GSTIN: The GSTIN of the taxpayer will automatically be filled in when the return is filed.
Name of the Taxpayer: The legal and trade name of the taxpayer will automatically be filled in when the return is filed.
Aggregate Turnover Details: The total turnover from the previous financial year will automatically fill in. The ARN and ARN date will also be filled in after filing.
Table 4: Inward supplies, including supplies on which tax is paid on reverse charge
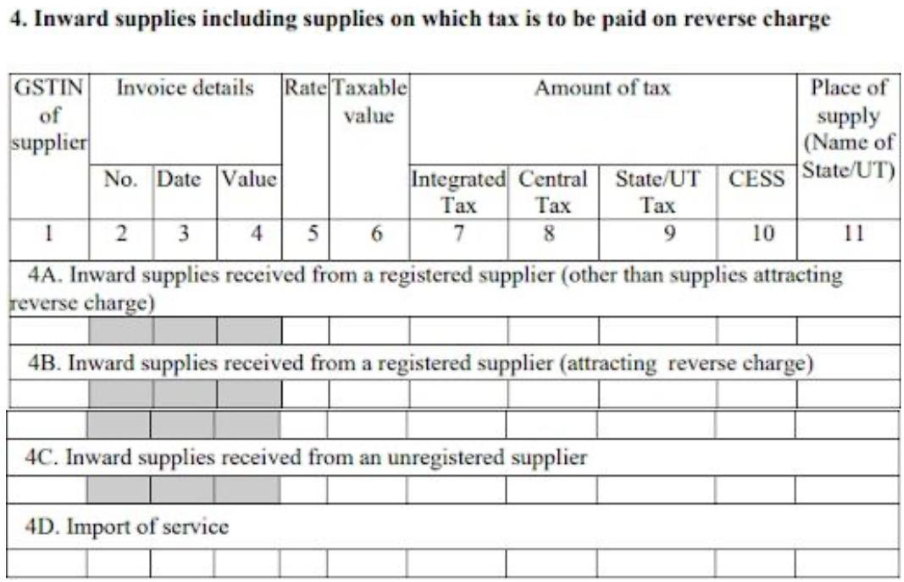
4A: Supplies from a registered supplier (no reverse charge)
The taxpayer needs to provide details of all supplies received from a registered supplier (both interstate and intrastate) where a reverse charge does not apply.
4B: Supplies from a registered supplier (reverse charge applies)
The taxpayer needs to provide details of all supplies received from a registered supplier (both interstate and intrastate) where a reverse charge applies.
4C: Supplies from an unregistered supplier
The taxpayer needs to provide details of all supplies received from an unregistered supplier, including both interstate and intrastate supplies.
4D: Import of services
The taxpayer needs to provide details of all imported services on which tax must be paid due to the reverse charge mechanism.
Table 5: Summary of self-assessed liability from form GST CMP-08
The information in this table will be automatically filled from Form GST CMP-08. This form is used to make payments every quarter. The table will summarize all the payment details from the CMP-08 forms filed during the year, including payments made on outward supplies, inward supplies with reverse charge, tax paid, and interest paid.
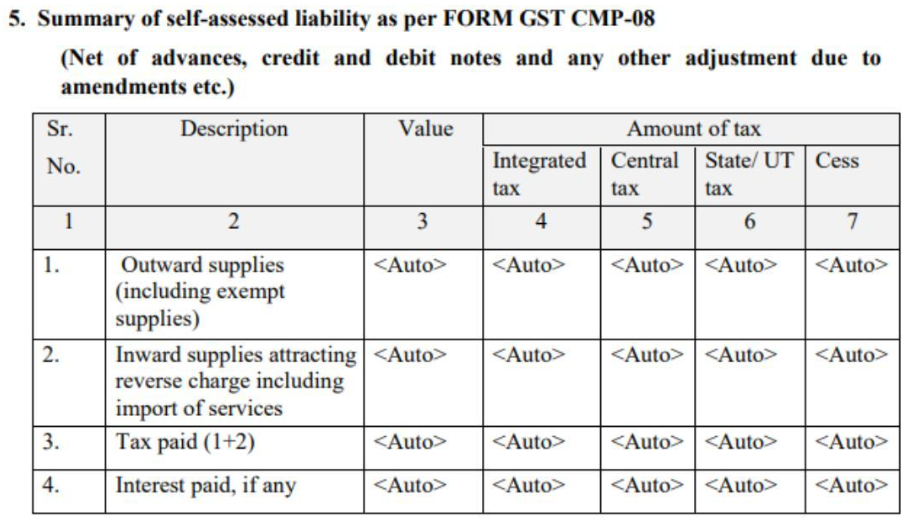
Table 6: Tax rate-wise details of outward and reverse charge inward supplies for the year
The taxpayer needs to enter details of all outward and inward supplies where a reverse charge applies, based on different tax rates. The total taxable value must be mentioned. The amounts for IGST, CGST, SGST, and Cess will be filled in automatically.
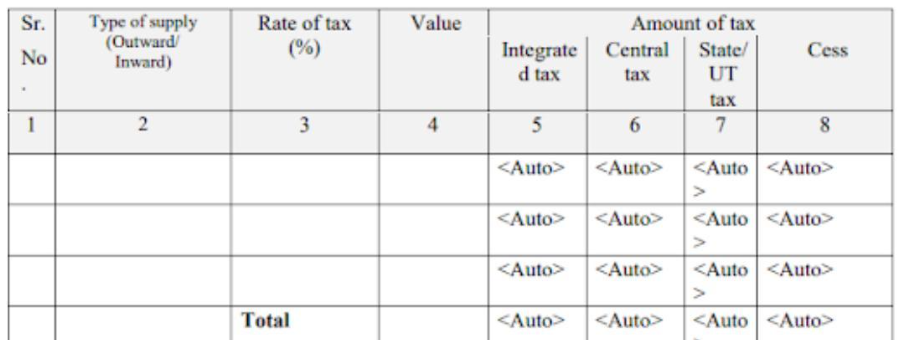
Table 7: TDS/TCS credit received
This table will automatically show any TDS or TCS credit received from a supplier or an e-commerce platform. The taxpayer needs to enter the GSTIN of the person who deducted the tax, the total invoice amount, and the TDS amount deducted.
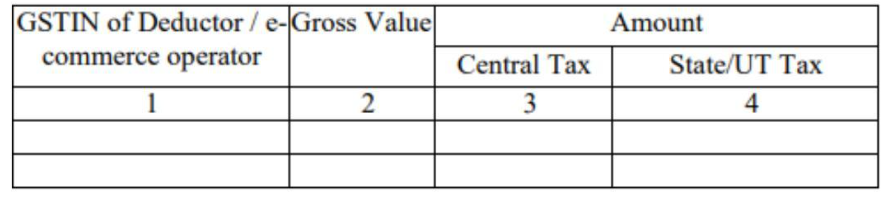
Table 8: Tax, interest, and late fee – payable and paid
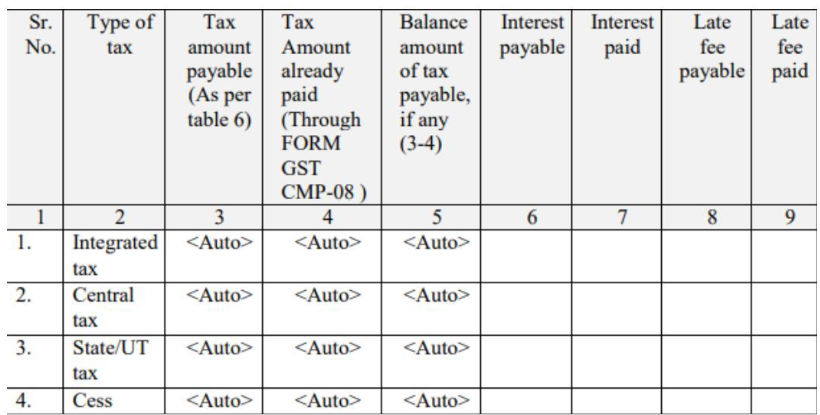
Tax amount payable: This amount will be auto-filled based on the details in Table 6.
Tax amount already paid: This will be auto-filled from the payments made in Form GST CMP-08.
Balance tax payable: This is the remaining tax to be paid, calculated by subtracting the paid amount from the payable amount.
Interest payable and paid: Enter the interest due for late return filing and the amount of interest actually paid.
Late fee payable and paid: Mention the late fee charged for delayed GST payment and the fee that has been paid.
Tax head breakup: The amounts paid under IGST, CGST, SGST, and Cess should be shown separately.
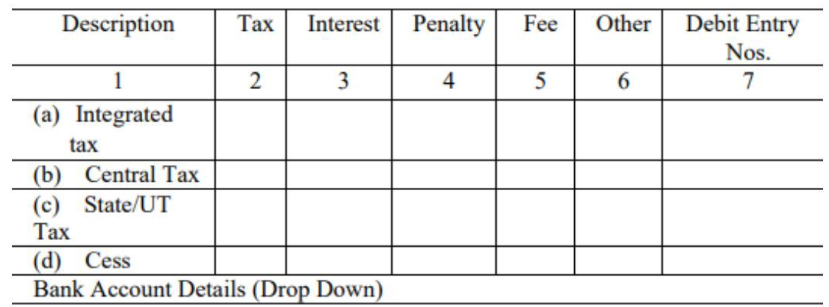
Table 9: Refund claimed from electronic cash ledger
If you have paid more tax than required, you can claim a refund using this table. The refund amount should be separated into different parts—tax, interest, penalty, fee, and any other charges.
How to file GSTR-4?
Filing GSTR-4 may sound complicated at first, but once you know the steps, it’s quite manageable as it only needs to be done once a year. Let’s walk you through the process:
Step 1: Log in to the GST portal
Start by visiting the official GST website services.gst.gov.in
Enter your username and password to access your dashboard.
Step 2: Go to the GSTR-4 filing section
Once you're logged in, follow these steps:
Go to the top menu, click on ‘Services’ > ‘Returns’ > ‘Annual Return’, then select your financial year.
This will open the return filing page where you can begin filling in your details.
Step 3: Select the financial year
After clicking on Here, you need to select the financial year for which you want to file the GSTR-4 (Annual Return).
After the list of applicable return forms appears, click ‘Prepare Online’ next to GSTR-4 – Annual Return to begin filing for the chosen year.
Step 4: Enter the aggregate turnover of the previous financial year
On the GSTR-4 return page, you’ll be asked to enter the aggregate turnover (i.e., total sales or revenue) from the previous financial year.
Enter the total turnover amount in the box (or 0 if none—do not leave it blank), then click ‘SAVE’ to proceed.
Step 5: Fill in the required details
The GSTR-4 return is divided into different tables or sections. You’ll need to enter information such as:
- Purchases made from registered and unregistered suppliers
- Inward supplies where a reverse charge is applicable
- Outward supplies (sales) made during the year
- Tax already paid through CMP-08 during the year
- Any TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) or TCS (Tax Collected at Source) credit received
- Details of tax payable, interest, or late fees, if any
- Refunds can be claimed if excess tax was paid
Step 6: Save your entries
After completing each section, don’t forget to click ‘Save’. This ensures your data isn’t lost if you get logged out or there’s a connection issue.
Step 7: Preview before submitting
Once all details are filled in, click ‘Preview Draft GSTR-4’.A PDF will be generated showing everything you’ve entered.
Take a few minutes to carefully review this file. Look for any mistakes or missing data, and go back to correct them if needed.
Step 8: Submit and file the return
Click ‘Submit’ to lock your return (it becomes non-editable), then click ‘File Return’ to complete the process.
You’ll be asked to sign the return using either:
- DSC (Digital Signature Certificate): commonly used by companies
- EVC (Electronic Verification Code): works with your OTP on phone/email
Once the return is filed successfully, you’ll receive an Acknowledgement Reference Number (ARN). This is proof that your GSTR-4 has been filed.
Step 9: Download and keep a copy
Make sure to download the final version of the return and keep it saved on your device. It’s important to have it for future reference or in case of any notice from the GST department.
Some tips to make filing easier:
- Keep all your purchase and sales invoices ready before you start
- Maintain records of your quarterly CMP-08 payments
- Double-check your tax and interest calculations
- File before the due date to avoid late fees and penalties
Due Date, Late Fees, & Penalties
The due date for filing GSTR 4 was 18th of the month after the end of the quarter. Now GSTR-4 being made annually, it should be filed by 30th April for every financial year by the composition dealers.
On a quarterly basis, Form GST CMP-08 needs to be filed by 18th of the month after the end of the quarter.
Common mistakes to avoid in GSTR-4 filing
When filing GSTR-4, which is for taxpayers under the composition scheme, it’s common to make some common mistakes. These can lead to fines or rejections. Here are the mistakes you should avoid:
- Incorrect tax rates: Sometimes, taxpayers use the wrong tax rates when filling out GSTR-4. Always make sure you're using the correct rate according to the goods or services you're providing.
- Missed-out returns: If you forget to fill out or submit any of the required returns or details, it can cause delays or penalties. Double-check that you've filled out everything.
- Wrong GSTIN: Make sure you are using your correct GST Identification Number (GSTIN). If it's incorrect, your filing will be rejected.
- Failure to report sales: Not reporting all your sales or reporting them incorrectly is a big mistake. Be accurate and include all sales made during the period.
- Not matching with books of accounts: Ensure that the details you provide in GSTR-4 match the figures in your accounting books. Discrepancies can cause problems.
- Incorrect HSN code: Using the wrong HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes for your products or services can lead to incorrect tax calculations.
- Not updating details: If your business details change, like address or business name, make sure to update them in your GST profile to avoid complications.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can file your GSTR-4 smoothly and stay compliant with GST rules.
FAQs
Is GSTR-4 monthly or quarterly?
GSTR-4 is now filed annually. Previously, it was filed quarterly. However, CMP-08 is still filed quarterly.
What is the turnover limit for GSTR-4 eligibility?
Businesses with an annual turnover of less than INR 1.5 crore can choose the Composition Scheme and file GSTR-4.
What is the difference between GSTR-4 and GSTR-9A?
GSTR-4 is the annual return for businesses under the composition scheme. GSTR-9A was also an annual return for composition dealers, but it has now been discontinued.
What is the difference between GSTR-3B and GSTR-4?
GSTR-3B is a monthly return for regular taxpayers. GSTR-4, on the other hand, is an annual return for businesses under the composition scheme.
What if GSTR - 4 filing is not done?
A penalty of INR 200 per day is levied, up to a maximum penalty of INR 5,000 if GSTR-4 is not filed.
How to revise GSTR - 4?
GSTR-4 cannot be revised after filing on the GSTN Portal.
Read More on GST Returns
GST Returns, Types of GST Returns, New GST Returns & Forms, Sahaj GST Returns, Sugam GST Returns, GSTR 1, GSTR 2, GSTR 3B, GSTR 5, GSTR 5A, GSTR 6, GSTR 7, GSTR 8, GSTR 9, GSTR 10, GSTR 11
GST
GST Software, GST Calculator, GST on Freight, GST on Ecommerce, GST Impact on TCS, GST Impact on TDS, GST Exempted Goods & Services, Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST, GST Declaration
Types of GST
CGST, SGST, IGST, UTGST, Difference between CGST, SGST & IGST
GST Rates & Charges
GST Rates, GST Rate Finder, GST Rate on Labour Charges, HSN Codes, SAC Codes, GST State Codes