E-invoicing under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime has revolutionized the way businesses manage their invoicing processes. It is a system that mandates the generation of invoices in a standardized electronic format, ensuring compliance and reducing errors. As of now, e-invoicing has become mandatory for businesses with an annual turnover exceeding ₹10 crores, making it essential for these entities to understand the e-invoice format to comply with GST regulations effectively.
In 2024, updates to e-invoicing regulations may include adjustments to turnover thresholds or changes in compliance requirements, emphasizing the need for businesses to stay informed about the latest developments.
What is E-Invoice in GST?
e-Invoice known as ‘Electronic invoicing’ is a system in which all B2B invoices are electronically uploaded and authenticated by the designated portal. It adheres to a specific format prescribed by the GST authorities.
| Best e-Invoicing Software Solution for Businesses in India | Generate e-Invoice Instantly in TallyPrime |
It plays a crucial role in the GST ecosystem by facilitating seamless data exchange between suppliers and tax authorities. E-invoicing integrates with the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP), where each e-invoice is assigned a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN). Additionally, a QR code is generated, which contains essential details about the invoice, ensuring easy verification by tax authorities.
Know more on IRN, Format, and process to generate it.
Key Components of an E-Invoice
The following are the 30 mandatory fields of an e-invoice. Earlier, 50 fields were to be mandatorily filled by the taxpayer.
|
Field name |
Description |
|
Document Type Code |
Every type of document has a code and this must be specified in this portion. |
|
Supplier Legal Name |
The name of the supplier according to the PAN card details. |
|
Supplier GSTIN |
The supplier GSTIN for e-invoice. |
|
Supplier Address |
The full address of the supplier including flat number, building no. etc. |
|
Supplier Place |
The city/village/town of the supplier must be specified here. |
|
Supplier State Code |
The state must be selected. |
|
Supplier Pincode |
The six-digit PIN code of the supplier’s address. |
|
Document Number |
A unique invoice number that makes sense to the business. It has to be sequential for easy identification. |
|
Preceding Invoice Reference and Date |
The original invoice details are being edited using a document such as a credit note. |
|
Document Date |
The date on which the invoice was issued. |
|
Recipient Legal Name |
The name of the buyer is specified as per his PAN card. |
|
Recipient’s GSTIN |
The buyer’s GSTIN needs to be specified. |
|
Recipient’s Address |
The detailed address of the buyer has to be specified. |
|
Recipient’s State Code |
The place of supply has to be specified. |
|
Place of Supply State Code |
The state of the recipient has to be selected. |
|
Pincode |
The location of the recipient has to be selected. |
|
Recipient Place |
The village/town/city of the recipient has to be specified. |
|
Invoice Reference Number or IRN |
The supplier leaves the field empty at the time of registration, and after that, GSTIN generates a unique number when the e-invoice is uploaded on the GSTN portal. As the e-invoice is accepted, acknowledgment is sent. Before the use of an e-invoice, the IRN has to be displayed on it. |
|
Shipping To GSTIN |
GSTIN of the person the item is being delivered to. |
|
Shipping To State, Pincode and State Code |
This field specifies the place where the goods and services are delivered. |
|
Dispatch From Name, Address, Place, and Pincode |
The name of the dispatching entity, along with the city/town/village specifics. |
|
Is Service |
If the supply of service has to be specified. |
|
Supply Type Code |
The type of supply and its responding code is specified. It can be supplied to SEZ, B2B, etc. |
|
Item Description |
The item’s description. |
|
HSN Code |
The particular code for the goods or services. |
|
Item Price |
The GST exclusive unit price prior to the item price discount being subtracted. This value must be positive. |
|
Assessable Value |
The item’s price excluding GST and after the item price discount has been subtracted. |
|
GST Rate |
The rate of the specific item for which the invoice has been generated. |
|
IGST Value, CGST Value and SGST Value Separately |
Every item must have IGST, SGST, and CGST. |
|
Total Invoice Value |
The total value, including GST. |
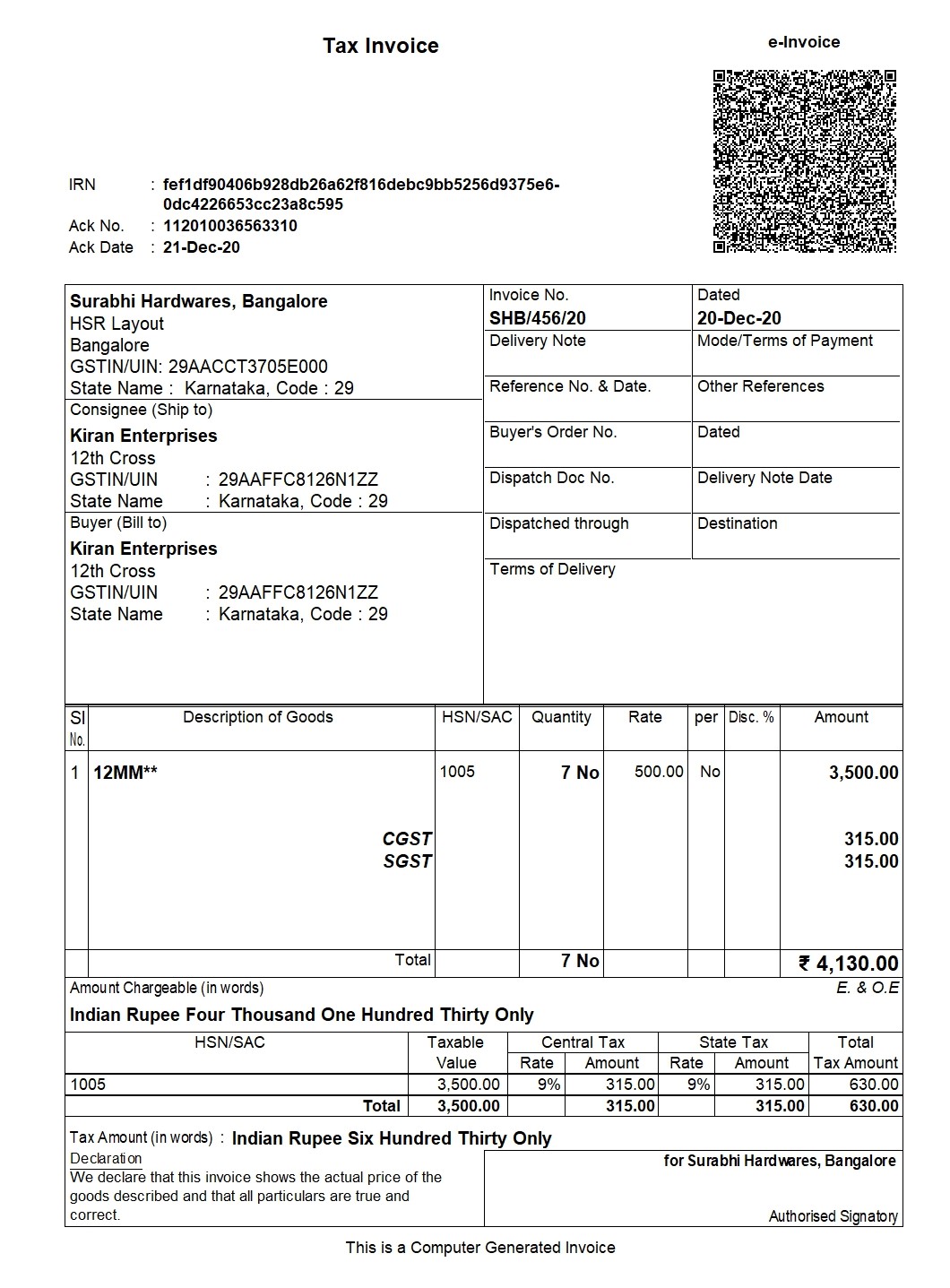
How Does E-Invoicing Work?
Step 1 – Generation of e-invoice:
The taxpayer will continue to generate invoices in the normal course of business. However, the reporting of these invoices electronically has criteria. It needs to be done as per the e-invoice schema, along with mandatory parameters. The mandatory fields of an invoice for the supply of goods are listed below:
-
- Invoice type
- Code for invoice type
- Invoice Number
- Invoice Date
- Supplier details like Name, GSTIN of Supplier, and Supplier address (including place, pin code, and state)
- Details of the buyer, such as name, GSTIN, state code, address, place, pin code, payee name, account number, payment mode, and IFSC code
- Dispatch details
- Invoice item being dispatched
- Total tax amount paid amount, and payment due
- Tax scheme (whether GST, Excise Custom, VAT)
- ‘Shipping To’ details like Name, GSTIN, address, pin code, state, supply type, and transaction mode (whether regular, ‘bill to’ or ‘ship to’)
- Details of goods like Sl. no., quantity, rate, assessable value, GST rate, amount of CGST/SGST/IGST, total invoice value, batch number/name
The seller has to ensure that his accounting/billing software is capable of generating a JSON of the final invoice. The seller can create a JSON following the e-invoice schema and mandatory parameters by using the following modes:
-
- Accounting and billing system that offers this service
- Utility to interact with either accounting/billing system, ERP, excel/word document, or a mobile app
- Offline Tool to generate e-invoice by keying-in invoice data
Step 2 – Generation of unique IRN:
The supplier has the option to generate a ‘hash’ based on specific parameters, usually three of them, such as Supplier’s GSTIN, Supplier’s invoice number, Financial Year (YYYY-YY). The prescribed algorithm, such as SHA256 must be used for the hash generation. If the hash is validated, it will later become the Invoice Reference Number (IRN) of the e-invoice.
Step 3 – Uploading the JSON:
The following modes may be used to upload the JSON of the final invoice:
-
- Directly on the IRP
- Through GST Suvidha Provider (GSP)
- Third-party provided apps (including through API)
- The supplier can also upload the hash along with the JSON onto the IRP if generated by him
Step 4 – Hash generation/validation:
The hash will have to be generated by the IRP in respect of the invoices uploaded without the hash. In such a case, the hash generated by the IRP would become the IRN. Where the supplier has also uploaded the hash, a de-duplication check will be performed. It is done by validating the hash/IRN against the Central Registry of the GST System to ensure that the IRN is unique. Once validated, the hash/IRN is stored in the Central Registry. IRP will then generate a QR Code and digitally sign the invoice and make it available to the supplier. The IRP also sends the e-invoice via e-mail mentioned on the invoice to the buyer and seller.
Benefits of E-Invoicing
The basic aim behind the adoption of the e-invoice system is to pre-populate the returns and reduce the reconciliation challenges. This is achieved by the design of the IRP system which shares the invoice data to the GST system and e-way bill system. Thus, continuous uploading of invoices will ensure that most of the details required in returns as well in the e-way bill get auto-populated.
The following are some of the key benefits of e-invoicing:
- Reduces reporting of same invoice details multiple times in different forms. It’s just a one-time upload and everything, as required, will get pre-populated.
- Part-A of e-Way bill will be auto-captured and only transporter details are required to be updated.
- On uploading of invoices, the B2B details will be auto-captured in GSTR-1 return.
- Substantial reduction in input credit verification challenges as the same data will get reported to the tax department as well to the buyer in his inward supply (purchase) register (GSTR-2A).
- On receipt of info from the GST System, a buyer can do a reconciliation with his Purchase register and accept/reject it on time under New Return.
- A complete trail of B2B invoices and system-level matching of input credit and output tax helps to reduce tax evasion.
- Increase efficiency in tax administration by eliminating fake invoices.
Compliance Requirements
E-invoicing is mandatory for GST-registered entities whose gross annual turnover exceeds ₹5 crore in any financial year since 2017-18. The rule came into effect on August 1, 2023. The change has been made through Notice No. 10/2023 – Indian Taxation System, which intends to boost compliance and facilitate the digitalization of business transactions.
Mandatory E-Invoicing Thresholds and Regulations
Current Threshold
- Threshold Limit: Entities whose annual gross revenue exceeds ₹5 crore require the generation of e-invoices for all B2B transactions.
- Previous Threshold: Previously, before the amendment in August 2023, the threshold was set at ₹10 crore.
Applicability
E-invoicing would be required for all GST-registered businesses whose turnover exceeded ₹5 crore in any financial year during the period from 2017-18 to date.
Aggregate turnover growth means the total revenues across all GSTINs under one PAN in India.
Exemptions
Certain services may be exempt from e-invoicing requirements, e.g.
- Small taxpayers below the threshold limit.
- Specific sectors or types specified by the government.
Read Articles
- How to Generate e-Invoice in GST?
- Generate e-Invoice Instantly in TallyPrime
- Bulk Generation of e-Invoices in TallyPrime
- How does e-Invoice System Work
- How to amend or modify e-invoices?
- How to Transit to e-Invoice System?
- Things to consider while choosing an e-invoice solution
FAQs on e-invoice
Can an e-invoice be canceled partially/fully?
You cannot cancel an e-invoice partially. If you must cancel an e-invoice, then it must be done completely. When you do this, you must report it to the IRN within 24 hours of the cancellation. If you try to cancel an e-invoice after that period, then you cannot use the IRN. Instead, you need to use the GST portal for cancellation, and it must be done manually. This has to be done prior to filing the returns. When you cancel, you cannot re-use the invoice number, and a new one must be generated else the IRP will reject it.
How does e-invoice work?
e-Invoicing works in two parts - first is the interaction between the business and IRP, and the second is the interaction between the IRP, the GST/E-Way Bill Systems, and the Buyer.
Why is e-invoicing needed?
E-invoicing helps organizations simplify their invoicing process, thus reducing paperwork and improving the time required for invoice processing.
Is e-way bill required for e-invoice?
Taxpayers have the option of generating an e-way bill when they generate an e-invoice. But they can choose to generate an e-way bill at a later time too. An e-invoice is needed along with an e-way bill to ensure the e-way bill is valid. Many assume that the e-way bill has become obsolete since the introduction of e-invoicing but that is not true. E-way bills are required for the transportation of goods is taking place and it is an important document.
Can we generate an e-invoice for an unregistered person?
The customer, or the unregistered person, will not be claiming an ITC. Currently, there is no provision in place whereby e-invoicing is mandatory for B2C transactions. But a dynamic QR code must be generated for digital payments whereby B2C transactions are concerned. This is mandatory for taxpayers with an aggregate turnover of over Rs. 500 crores since 1st December 2020.
Who should register for e-invoicing?
e-Invoicing has been mandated for businesses with an annual turnover exceeding Rs 10 crore from 1st October 2022, mandating all businesses under the said category to register for e-invoicing. And the businesses with an annual turnover exceeding Rs 5 crore will be mandated to issue e-invoices from 1st August 2023 in any preceding financial year from 2017-2018 onwards.
Where to register for e-invoicing?
All GST-registered taxpayers who are required to generate IRNs should register for e-invoicing using their GSTIN. Additionally, taxpayers who are registered on the e-way bill portal are not required to register on the e-invoice system; instead, they can use their EWB credentials to login.
What is e-invoice registration form?
e-Invoice registration form is the piece of document that you need to register in the e-invoice system.
How to generate e-invoice in the GST portal?
- Visit the e-invoice portal
- Click on the Registration button
- Click on e-Invoice Enablement
- Now, you need to enter the GSTIN of the company
- Post this; you'd need to get the OTP verification done
- Now, you need to enter the annual turnover details with the related financial year and submit
- Now you are registered for e-invoicing
- Now you can log in to the e-invoice portal and upload B2B invoices using a chosen mode to generate IRN
How to upload e-invoice in the GST portal?
- You need to login to your GST account
- Now, select the month for which you want to upload GST invoices
- Post this, select GSTR-1 Return and Click on Prepare Online
- Now you can select B2B invoices and enter details of the invoices one by one
How to print e-invoice in the GST portal?
- Enter invoice details
- preview and confirmation
- Validation and generation of JSON File
- Login to e-Invoice Portal
- Upload JSON file, and generate IRN, and download response file
- Import IRNs in GePP and push to history
- Print e-Invoice
How to modify e-invoice in gst portal?
What are the modes of generating e-Invoice?
Multiple modes will be made available so that the taxpayer can use the best mode based on his/her need. The following are different modes of generating e-Invoice.
- Web-Based,
- API Based,
- SMS Based,
- Mobile App
- offline tool based and
- GSP based
Watch How to Set-up TallyPrime for e-invoice
Video guide - e-invoicing in TallyPrime
Know more about e-invoices in GST











