- GST Invoice
- GST Invoice Format
- Time Limit of issuing the GST Invoice
- Copies of the GST Invoice required
- GST Invoice Rules
With GST around the corner, it is extremely critical for businesses to start invoicing under GST mode, and not face any roadblocks, as they usher in the new age. Businesses will need to ensure that the GST transaction invoices are passed with the requisite details, which will later enable them to claim the right ITC and remain GST compliant while growing continuously.
What is GST invoice?
When a registered taxable person supplies taxable goods or services, a GST invoice is issued. To issue and receive a GST compliant invoice is a prerequisite to claim ITC. If a taxpayer does not issue such an invoice to his customer - who is a registered taxable person, his customer loses the ITC claim and the taxpayer loses its customers.
Key Components of a GST Invoice
A GST invoice must include several mandatory fields to ensure compliance and accurate tax reporting:
- Invoice number and date
- Customer name
- Shipping and billing address
- Customer and taxpayer's GSTIN
- Place of supply
- HSN code
- Taxable value and discounts
- Rate and amount of taxes i.e. CGST + SGST/UTGST (intra-state) OR IGST (inter-state)
- Item details i.e. description, unit price, quantity
- Optional fields may include discounts, payment terms, and additional notes.
These elements capture supplier/buyer details, transaction specifics, HSN classification, and precise tax breakdowns (CGST/SGST/IGST), enabling seamless GST compliance, ITC claims, and audit verification.
E-invoicing helps organizations simplify their invoicing process, thus reducing paperwork and improving the time required for invoice processing.
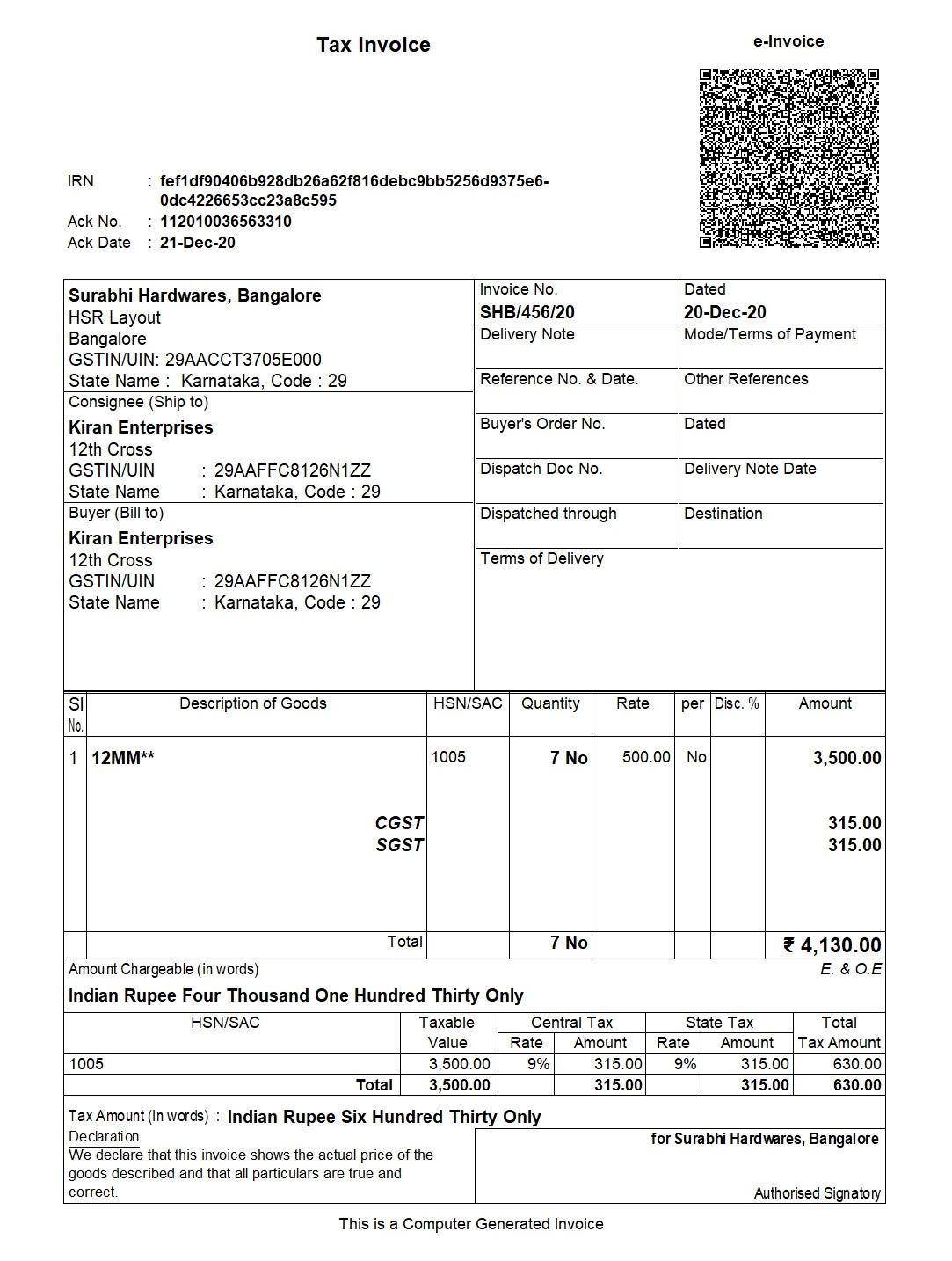
e-Invoice generated in TallyPrime
GST Invoice Formats
Different formats exist for various transactions:
GST Invoice Format for Goods
This format is used when selling goods under GST regulations. It includes details about the seller, buyer, goods supplied and applicable taxes.
Key Elements:
- Supplier’s and buyer’s name, address, and GSTIN.
- Unique invoice number and date.
- Description of goods, HSN code, quantity, and unit price.
- Total taxable value and tax breakup (CGST, SGST, IGST).
- Place of supply (for inter-state sales).
GST Invoice Format for Services
This format is tailored for businesses offering services, focusing on service-related details instead of goods.
Key Elements:
- Supplier’s and recipient’s name, address, and GSTIN.
- Unique invoice number and date.
- Description of services, SAC code, and service value.
- Applicable GST rates and breakup (CGST, SGST, IGST).
- Terms of payment (e.g., advance payment or full payment).
Special Formats:
Export GST Invoice Format
Used for exporting goods or services. It must mention “Export Without Payment of Tax” or “Export With Payment of Tax,” depending on whether IGST is charged.
Key Elements:
- Supplier’s and recipient’s details, including country of export.
- HSN/SAC code and taxable value.
- Mention of shipping bill details or bill of export.
- Tax breakup (if applicable).
Reverse Charge Invoice Format
Applicable when the recipient is liable to pay GST under the reverse charge mechanism.
Key Elements:
- Standard invoice details with a clear mention of “Reverse Charge”.
- Taxable value of the goods or services.
- Place of supply and GST rates.
ISD (Input Service Distributor) Invoice Format
Used by ISDs to distribute input tax credits (ITC) across multiple branches or units.
Key Elements:
- ISD’s and recipient unit’s GSTIN.
- Details of eligible and ineligible ITC.
- Invoice number, date, and taxable amount.
GST Invoice Types
Businesses are required to issue different types of invoices based on the nature of the transaction. Each invoice type serves a specific purpose and ensures compliance with GST laws. Let’s look at the major types:
1.Tax Invoice
A Tax Invoice is the most common type of GST invoice issued when a registered business sells taxable goods or services.
It includes key details such as the GSTIN, invoice number, date, description of goods/services, tax rate, and total amount payable.
2. Bill of Supply
A Bill of Supply is issued when a seller is not allowed to charge GST on the transaction.
This applies to businesses registered under the Composition Scheme
3. Aggregate Invoice
An Aggregate Invoice is issued when multiple small-value invoices (each below ₹200) are combined into a single invoice for the day.
For example, a retailer making several small B2C sales can issue one aggregate invoice at the end of the day instead of creating multiple individual invoices.
4. Reverse Charge Invoice
A Reverse Charge Invoice is used when the tax liability shifts from the supplier to the recipient under the Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM).
In such cases, the buyer is responsible for paying the GST directly to the government.
5. Debit Note and Credit Note
A Debit Note is issued by the seller when the taxable value or tax charged in the original invoice is less than the actual amount. It increases the buyer’s liability.
A Credit Note is issued when the taxable value or tax charged is more than the actual amount, such as during returns, discounts, or overbilling.
Time limit of issuing the GST invoice
|
Supply of Goods |
Supply of Services |
|
The tax invoice must be issued before or at the time of -
|
The tax invoice must be issued within -
|
GST Invoice Rules for Small Businesses and Startups
Small businesses and MSMEs benefit from simplified invoicing rules under certain turnover limits. Understanding these thresholds can help startups navigate compliance more easily.
|
Composition Scheme |
Businesses under the Composition Scheme are exempt from issuing GST invoices but must issue a Bill of Supply. |
|
E-Invoicing Exemption |
MSMEs with turnover below ₹5 crore are exempt from mandatory e-invoicing requirements. |
|
Optional GST Registration |
Businesses with turnover below the exemption limit are not required to register for GST. |
Turnover Limits and Implications
- Exemption Threshold: GST registration is not mandatory for businesses with annual turnover below ₹20 lakh (₹40 lakh for goods in some states).
- E-Invoicing Threshold: E-invoicing is mandatory for businesses with annual turnover above ₹5 crore.
- Composition Scheme Eligibility: Businesses with annual turnover up to ₹1.5 crore can opt for the Composition Scheme.
- Filing Requirements: Simplified GST returns (e.g., GSTR-4) for those under the Composition Scheme.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in GST Invoicing
|
Incorrect GSTIN Entry |
Double-check GSTINs of both seller and buyer before finalizing the invoice. |
|
Missing Mandatory Fields |
Ensure invoices include all mandatory details such as invoice number, date, GSTIN, HSN code, and taxable amount. |
|
Wrong HSN/SAC Code |
Use the correct HSN/SAC codes based on the nature of goods/services. Refer to the GST rate schedule. |
|
Mismatched Tax Rates |
Verify applicable GST rates (e.g., 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%) for the product/service being invoiced. |
|
Failure to Issue a Bill of Supply (if needed) |
Issue a Bill of Supply for exempted goods/services or under the Composition Scheme. |
|
Incorrect Tax Calculation |
Use GST-compliant software/tools to automatically calculate SGST, CGST, and IGST accurately. |
|
Late Issuance of Invoices |
Generate invoices within the prescribed time limit (e.g., 30 days for services). |
|
Missing Reverse Charge Details |
Clearly indicate "Subject to Reverse Charge" when applicable on the invoice. |
|
Non-Compliant Invoice Format |
Follow the GST-compliant format with clearly segmenting tax components (CGST, SGST, IGST). |
|
Overlooking E-Invoicing Requirements |
Verify if e-invoicing applies to your turnover bracket and generate compliant e-invoices. |
Electronic GST Invoicing (e-Invoicing)
The e-invoicing system allows businesses to generate invoices electronically, which are then validated by the GST Network (GSTN). As of now, businesses with a turnover above ₹10 crore are required to use e-invoicing. TallyPrime integrates seamlessly with this system, simplifying compliance.
Applicability of e-Invoicing
e-Invoicing is mandatory for businesses with an annual aggregate turnover exceeding ₹5 crore (as of 2023). This threshold ensures that medium and large businesses adhere to e-invoicing, improving tax compliance across the ecosystem. Certain entities, such as businesses registered under the Composition Scheme, SEZ units, and government departments, are exempt from e-invoicing requirements.
How e-Invoicing Works in Tally
Step 1- Activation: Users activate the e-invoicing feature in Tally's settings.
Step 2- Data Upload: GST invoice details are automatically uploaded to the IRP.
Step 3- IRN and QR Code: The IRP generates the unique IRN and QR code, which are retrieved and embedded in the invoice.
Step 4- GST Filing Integration: The e-invoicing process syncs with GST return filings, populating details in GSTR-1.
How to Generate a GST Invoice Using TallyPrime
Generating a GST invoice using TallyPrime is straightforward:
Step 1- Set Up GST in TallyPrime
Before you start generating invoices, ensure that GST is enabled in TallyPrime and your company details are configured for GST compliance.
Enable GST:
- Open TallyPrime and go to Company Information.
- Under the Statutory and Taxation section, enable GST.
- Enter your GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) for your company and, if applicable, your GST registration type (e.g., Regular, Composition, etc.).
Set GST Rates:
Go to Accounting Masters and set up the GST rates applicable to your products or services. TallyPrime provides predefined GST tax rates (e.g., 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%), or you can create your own based on your needs.
Configure Stock Items (For Goods):
- If you are invoicing goods, create the stock items and assign them the relevant HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) code and applicable GST rates.
- For services, you’ll need to configure the service items and assign them the appropriate SAC (Services Accounting Code) and GST rates.
Step 2- Create or Select a Ledger for GST Invoice
You need to ensure that all the ledgers involved in the transaction are set up correctly with the appropriate GST details:
- Go to Create Ledger under Accounts Info.
- Create ledgers for Sales, GST Receivable, and GST Payable (if they aren't already set).
- Assign GST Classification to each ledger (e.g., Output GST, Input GST, CGST, SGST, IGST, etc.).
- Ensure that the party ledger (customer or supplier) has the GSTIN and correct place of supply information.
Step 3- Start the GST Invoice
Once the setup is complete, you can start generating your GST invoice:
- Go to the Gateway of Tally and select Vouchers.
- Choose the type of voucher:
- For sales of goods, select Sales Voucher (F8).
- For sales of services, also use Sales Voucher but ensure you select the correct service items.
- Fill in the Invoice Details:
- Party Name: Select the customer from the Ledger list.
- Date: Set the correct invoice date.
- Item Details: Enter the products or services you're selling.
- For goods, select the stock item and enter the quantity, rate, and taxable value.
- For services, select the service item, and enter the service value and applicable GST rates (CGST, SGST, or IGST).
- GST Calculation: TallyPrime will automatically calculate CGST, SGST, or IGST based on the state of supply.
- HSN/SAC Code: Tally will automatically fetch the correct HSN/SAC code based on your stock or service item setup.
- Check the Invoice Summary:
- Verify that the total taxable amount and GST breakup (CGST, SGST, IGST) are correctly calculated.
- If applicable, include any discounts or additional charges that affect the final amount.
Step 4- Finalize and Save the Invoice
- Once the details are filled in, press Enter to complete the transaction.
- TallyPrime will prompt you to save the invoice. You can also print the invoice directly from the voucher screen or email it to the customer.
- The system will generate a unique invoice number automatically, and you can also set a custom numbering system.
Step 5- Review and Reconcile
- After generating the GST invoice, you can go to the Sales Register or Ledger report to review and reconcile all GST transactions.
- TallyPrime ensures that the correct GST filing format (GSTR-1, GSTR-3B) is followed and facilitates seamless GST return filing.
Watch Video on Invoice Matching under GST
Know More about Invoices in GST
- E-Invoice in GST
- How to Generate E-Invoice in GST
- How to Transit to E-Invoice System
- Who Should Issue an E-Invoice in GST
- Working of E-Invoice System
- Date of implementing e-invoicing in GST
E-Way Bill
GST

















