Inventory management is one of the key factors which will define the success of the business. Inventory is money sitting around in another form and it holds huge working capital. Any inefficiency in managing inventory will put your business at a disadvantage. This article talks about the basics of inventory management.
Here are 8 Tips to become more efficient in Inventory Management
What is Inventory Management?
Inventory management can be defined as a whole lot of activities done to maintain an optimum number of inventories to ensure uninterrupted production, sales, high customer satisfaction, reduced inventory handling cost and so on.
In simple words, inventory management is all about striking the balance between overstocking and understocking. Overstocking will lead to cash flow blockage and additional cost for managing excess stock. On the flip side, understocking leads to loss of sale due to non-availability of stock at the right time.
Thus, it’s all about maintaining the right level inventories at the right time and keeping the inventory handling cost at low.
To be efficient in inventory management, a whole lot of activities/ techniques are to be followed by the business.
Why is inventory management important?
Inventory management determines the stock a business should keep and when it should replenish it. It aims to avoid understocking and overstocking for the proper functioning of the business while meeting customer demand at all times. Businesses that can manage inventory well function better because they don’t have unsold stock or deadstock in hand. A business should ideally have sufficient inventory to meet demand and be prepared for unforeseen circumstances when there is a demand surge.
Inventory management formulas determine the ideal amount of stock, when to replenish stock, and how much to keep aside to be prepared in case of emergencies. Depending on your inventory type, you keep, you can use some or all of the inventory formulas for better insights into your business inventory. Inventory management boosts revenue by selling the inventory at the right time. Inventory management applies to every business; whether you are an e-commerce business or even if you operate a brick-and-mortar store.
The Benefits of Inventory Management
Inventory management optimizes stock levels to meet demand while minimizing costs, crucial for businesses like those using TallyPrime for GST-compliant operations. It ensures seamless supply chains, reduces waste, and supports accurate bookkeeping in accounting workflows. Proper management aligns with GST inventory tracking for precise invoicing and compliance.
Effective inventory management delivers cost savings by preventing overstocking and stockouts. It boosts operational efficiency through real-time tracking and better demand forecasting. Businesses gain improved cash flow, higher customer satisfaction, and compliance advantages, especially for GST-registered entities managing input credits.
What are the challenges of inventory management?
Inventory management is a challenging process, and here are some reasons why.
Difficult to predict demand
Customer demand can change, and a lot of factors can affect demand. Take the pandemic for example. It changed consumer preferences and put the spotlight on certain essential products. As it is difficult to predict customer demand, managing inventory is a tough task because it is never guaranteed what a customer will want in the next instant.
Space utilization is tricky
The way the inventory is managed can be challenging, especially when a business has several product lines. Businesses need to use the warehouse space well otherwise it can easily lead to unsold stock. If the business has multiple warehouses, then it becomes trickier to store efficiently. A lot of time is required to properly manage every warehouse.
Determining stock in hand
Many methods of determining the inventory at hand exist. However, it is still a challenge many businesses struggle with because it is a tedious and time-intensive task. It is prone to error especially when there is no proper inventory management system in place. This can impact the other aspects of your business because your staff will spend mostof the time counting inventory.
Unexpected problems in the supply chain
If any disruptions occur in the supply chain, they will directly impact your business which can cause problems. Natural disasters and other problems can cause delays in receiving orders and disrupt your everyday business. It is difficult to always predict when a problem can happen and so businesses can never be fully prepared for it.
What is the process of inventory management?
The process of inventory management is as follows.
Step 1: Order inventory
The first step starts with you ordering raw materials and the required components you require for the finished goods.
Step 2: Monitor and store inventory
You will monitor the inventory you received from your supplier and then store it as required to ensure it is safe and easily retrievable. You will have a system in place for efficient inventory storage.
Step 3: Check inventory levels
You will check the inventory levels and keep them noted somewhere. You can use any inventory management software to reduce errors.
Step 4: Customers place orders
Customers place orders depending on where you are selling and setting up a storefront. These orders are then approved by a system.
Step 5: Send orders to customers
You then find the necessary items the customers ordered and send them to your customers after packaging.
Step 6: Update inventory level
When the item has been sent, you will update inventory levels, so it accurately reflects the inventory you now have at hand.
Step 7: Restock inventory
You are going to restock your inventory as required before the stocks are too low. Restock will depend on demand forecasting and other insights along with past orders.
Inventory Management Methods
Common methods include FIFO (First In, First Out) for perishable goods, LIFO (Last In, First Out) for fluctuating costs, and Just-In-Time (JIT) to minimize holding costs.
| Method | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| FIFO | Sells oldest stock first | Perishables, GST-valued goods |
| LIFO | Sells newest stock first | Non-perishables with inflation |
| JIT | Orders stock as needed | Lean manufacturing, low storage |
| ABC Analysis | Prioritizes high-value items | High-volume accounting firms |
Inventory management formulas
The main inventory management formulas are as follows.
Inventory turnover
Inventory turnover or stock turn shows the number of times items were sold and replaced over time. It can enable businesses to make informed pricing decisions and how much inventory to keep in stock. If the ratio is low, it means you have an overstocking situation and if the ratio is high it means you don’t have enough inventory. The inventory turnover can be calculated monthly. The formula for inventory turnover is as follows.
Inventory Turnover = Cost of goods sold / ((Beginning inventory) + (Ending inventory) / 2)
Economic order quantity or EOQ
The economic order quantity formula aims to reduce costs associated with stocking inventory. It reveals how much stock a company should keep. EOQ takes set-up costs, holding costs, and demand rate into consideration. The EOQ value highlights how much inventory a business should keep to meet customer demands at a certain time. The EOQ can be calculated as follows.
EOQ = Square root of (2 x Set-up costs x Quantity sold per year) / Holding costs
Sell through rate
Sell through rate lets you understand the inventory you sold after receiving it. It enables you to know the speed at which your finished goods turn to revenue. A low sell-through rate means you are overstocking or consumer demand has dipped. A high sell-through rate means you have sufficient inventory according to customer demand and the inventory is being utilized efficiently. The sell-through rate formula is as follows.
Sell Through Rate = (Number of units sold / Number of units received) x 100
Reorder point
The reorder point determines when you should stock inventory. It tells you when is the best time to reorder stock. Proper stock management is a major benefit of using this inventory management formula for your business but it is highly useful. If you have many product lines, then it can be a tedious task to compute the reorder point. The reorder point formula is as follows.
Reorder Point = Lead time demand + Safety stock
Safety stock
The safety stock is the stock you should keep away and might need at a later date in an emergency. Having some stock set aside prevents a zero inventory situation whereby no stock is available. This can happen when you are unable to manage your inventory due to supply chain disruption or an emergency has suddenly occurred. All businesses are recommended to calculate this to be better prepared. The safety stock formula is as follows.
Safety Stock = (Maximum daily usage x Maximum lead time) – (Average daily usage x Average lead time)
Add H2 "Inventory Management FAQs" right after current H2 "Inventory Classification"
Add H3 "FAQ 1 - What is the role of inventory management?
Inventory and stock are used interchangeably by many and experts say it is not wrong to do so because people use the word stock to mean inventory. However, there is a slight difference between the two. Stock means end products while inventory refers to materials used during production and the end products.
What is Inventory?
Inventory is an idle stock of physical goods that contain economic value and are held in various forms by an organization. Inventories are held in various forms, it can be a stock awaiting packing, processing, transformation, use or sale in a future point of time.
Any organization which is into production, trading, sales and service of a product will necessarily hold inventories to aid in future consumption and sale.
From the above definition of inventory, you can list down the following:
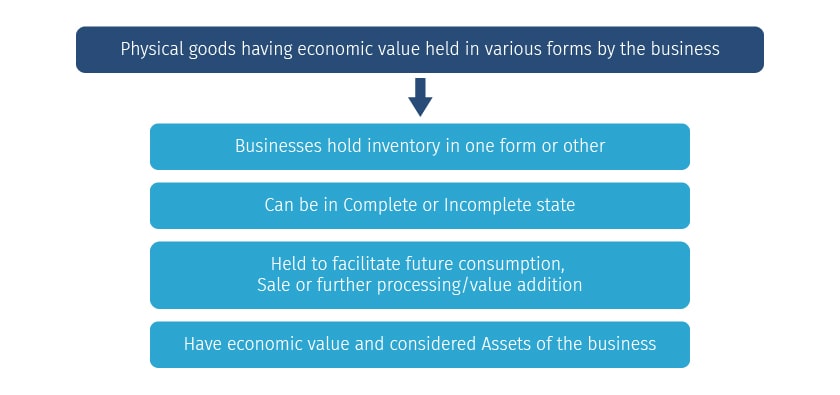
Inventory Types
One of crucial for efficient inventory management is to know and understand the different types of inventories you deal with. This because, importance, requirements, inventory level, treatment etc. differs basics the type of inventory. For example, the way you look at raw material differs from the finished product.
The following table explains the different types of inventory along with the examples.
|
Types of Inventory |
||
|
INPUT STAGE |
PROCESS STAGE |
OUTPUT STAGE |
|
Raw Materials |
Work-in-progress |
Finished Goods |
|
Consumables required for processing & manufacturing · Fuel, Stationary · Bolts & Nuts etc. |
Semi-Finished Production in various stages, lying with various departments like · Production · WIP Stores · QC · Final Assembly · Paint Shop · Packing · Outbound Store etc. |
Finished Goods at Distribution Centers throughout Supply Chain |
|
Maintenance Items/Consumables |
Production Waste and Scrap |
Finished Goods in transit |
|
Packing Materials |
Rejections and Defectives |
Finished Goods with Stockiest and Dealers |
|
Local purchased Items required for production |
|
Spare Parts Stocks & Bought Out items |
|
|
|
Defectives, Rejects and Sales Returns |
|
|
|
Repaired Stock and Parts |
|
|
|
Sales Promotion & Sample Stocks |
Transaction Types
Inventory transactions are used to track the quantities & movements of inventories. It’s not just your purchase or sale that becomes part of your inventory transaction types. While these are most frequent, but you got to deal with different inventory transaction types in accordance with the situation. The input from this becomes part of the key reports required for optimum inventory management.
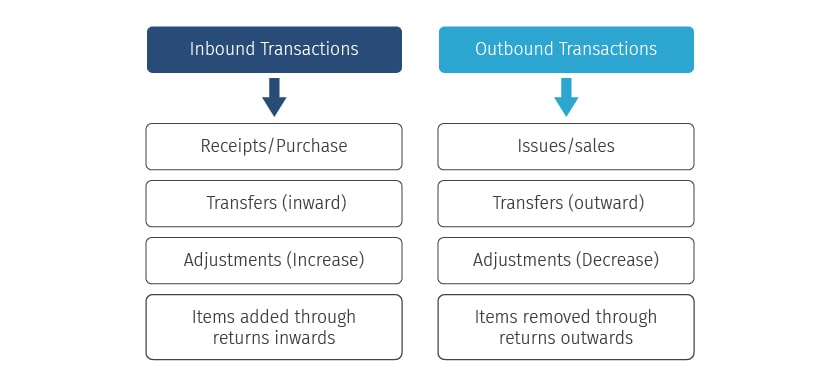
Inventory Classification
Inventory classification refers to the grouping of inventory for ease of identification, accessibility and differentiation by the nature of the stock, value, durability, etc. While there no standard that guides how once should classify the inventories but it is recommended that classification should be carried out basis the end objective you would like to achieve through this.
For example, if you would like to see the basis of the report the type of inventories, you can classify it as raw materials, work-in-progress and finished products. Similarly, you can classify it by brand, nature, size, colour etc.
Examples of Inventory Classification
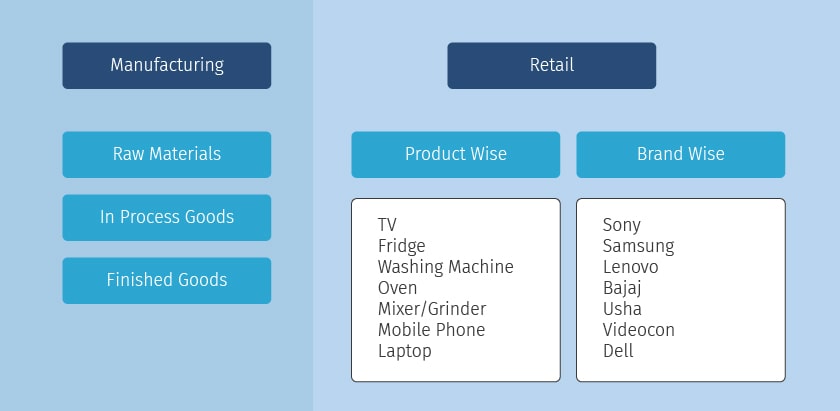
As shown in the above example, manufacture would classify the inventory basis the inventory types while a trader may classify based on the type of product or the brand he is dealing with. It is important to keep in mind the end objective while classifying the inventories. The better you classify your inventories; it becomes easier for you to read through the inventory reports.
Watch this Video to Know How to View and Analyse Inventory in TallyPrime
Read More on Inventory Management
- Inventory Management Techniques
- Inventory Reports
- Inventory Planning
- Inventory Valuation
- Inventory Control
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
- Importance & Benefits of Inventory Management
- How to Audit Inventory
- How Godown Summary Helps in Better Inventory Management

















