- What is revenue expenditure?
- Revenue expenditure types
- Example of revenue expenditure
- Revenue expenditure Vs. capital expenditure
- Both revenue expenditure and capital expenditure are equally important
What is revenue expenditure?
Revenue expenditures are short-term expenses that are also known as revenue expenses and operational expenses (OPEX). Revenue expenditure is generally spoken to in relation to fixed assets as it records the expenses which have occurred in connection to a fixed asset. For example, if you have a piece of equipment that requires monthly maintenance then the expense will be termed under revenue expenditure. It involves all costs that are required for the successful running of a business such as salaries for employees and property taxes. Revenue expenditure is recorded during an accounting period or a single year.
Revenue expenditure types
Revenue expenditure can be divided into two categories; direct expenses and indirect expenses.
Direct expenses
Direct expenses are those costs that are incurred when goods and services are in the process of being produced. The costs that are incurred during the day-to-day operations that take place in the business are also direct expenses. For manufacturing companies, examples of direct expenses include the costs that are incurred for the conversion of raw materials to finished products or goods. Direct expenses also include costs such as electricity used during the production, wages paid to workers, legal expenses, rent, shipping-related costs, and freight charges.
Indirect expenses
Indirect expenses are the second type of revenue expenditure. These types of expenses are usually incurred when the finished goods and services are being sold and distributed. These expenses include taxes, salaries for employees, depreciation, and interest among others. Indirect expenses also include repairs and maintenance costs. Although these costs aren’t directly linked to the finished products, they are required to ensure the proper functioning of the asset which in turn supports the proper functioning of the business.
Example of revenue expenditure
A company called A&J spends 100000 BDT on a machine used for the production of goods. To ensure the proper functioning of the machine, a monthly fee of 1000 BDT is spent. In this example, the revenue expenditure is 1000 BDT which has been spent on the upkeep of the machine on a monthly basis. When the income statement will be prepared, the 1000 BDT will have an entry for that particular month where the upkeep expenditure was made. In case the machine has an issue and needs to be repaired, the cost of repair will also fall under revenue expenditure and will be reflected on the month during which the expenditure was done.
Revenue expenditure Vs. capital expenditure
Revenue expenditure and capital expenditure are often confused for one another which makes understanding their differences even more vital.
|
Revenue expenditure |
Capital expenditure |
|
Functionality |
|
|
Revenue expenditure is the expense that is used to run your business on a daily basis. It includes the costs used to ensure the proper functioning of a fixed asset repair costs, maintenance costs, and costs that are incurred for current operations. It differs from the cost used to acquire or buy an asset. Examples of revenue expenditure include rent, utilities, and office supplies. |
Capital expenditure, also known as a capital expense or Capex, is the expense that is used to acquire a capital asset. This asset is a long-term asset that is used to improve how the business functions by boosting efficiency. Examples of capital expenditures include vehicles, computer equipment, land, fixtures, software, office buildings, and so on. |
|
Consumption |
|
|
Revenue expenditure is consumed within a short span of time. For example, the regular upkeep of equipment is done monthly or every quarter depending on the type of equipment used for the production of goods. Revenue expenditure is a recurring expense that your business needs to spend every month or every few months. It is not a one-time investment. |
Capital expenditure is consumed over a long period of time until the asset is useful or until the asset has reached its end of life. For example, machinery is used for many years until it is able to function correctly. It is not a recurring expense as your business needs to pay for the cost of the machinery only once. |
|
Reporting |
|
|
Revenue expenditure is reported in the income statement of your business whenever the expense was incurred. It is not stated in the balance sheet. When it comes to charging revenue expenditures, they are charged immediately in the current period during which you paid for it or after a short period of time. |
Capital expenditure is reported in the cash flow statement of your business and in the balance sheet. When being reported in the balance sheet, it is stated under fixed assets. Capital expenditure isn’t immediately charged as an expense. Instead, it is charged over a long period of time until you will use it using depreciation. This is a gradual process. |
|
Purpose |
|
|
The purpose of revenue expenditure is to ensure the assets such as machinery are functioning optimally at all times and so this expenditure comes into the picture after the business has started operating. These expenditures are used to sustain your business. Although these expenditures do not add more capability to the asset, they are used to ensure the asset works as it should. |
The purpose of capital expenditure is to generate more revenue over time. It involves expanding the business and investing in machinery that is going to give ROI and long-term gain. For example, an expensive machine in a manufacturing plant can be acquired to improve current processes so that it can contribute to revenue generation. These expenditures come into the picture before your business starts to operate. |
|
Cost |
|
|
When it comes to revenue expenditure, the cost associated with them is comparatively lower than that of capital expenditures. Revenue expenditure isn’t the expense related to investment so it is generally smaller. In certain cases, the expense related to revenue expenditures can be large as long as the cost is a period cost or it is an expense related to the revenue. |
Your business will pay much more for anything that falls under capital expenditure. Firms usually have a threshold value that marks the distinction between revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. If the expenditure is more than the threshold value then it is considered a capital expenditure, else it might be a revenue expenditure. |
Both revenue expenditure and capital expenditure are equally important
It is wrong to say that either is better than the other because both are required for your business to operate without issues and generate profits. Capital expenditure is critical because it can improve business efficiency. Revenue expenditure is vital as it ensures smooth business operations so there is nothing stopping your business from operating fully. Your business must manage and monitor both these expenditures to ensure you are not over-spending on each. If you do so regularly, you can effectively use strategies for regulating these expenses.
TallyPrime is an ERP accounting software that provides a powerful combination of ERP and accounting software. It can be of help when it comes to both revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. TallyPrime ensures you stay within your budget, know your spending history, and spend wisely. With the help of its robust reports, you get instant insights that can drive your business decisions in the right direction
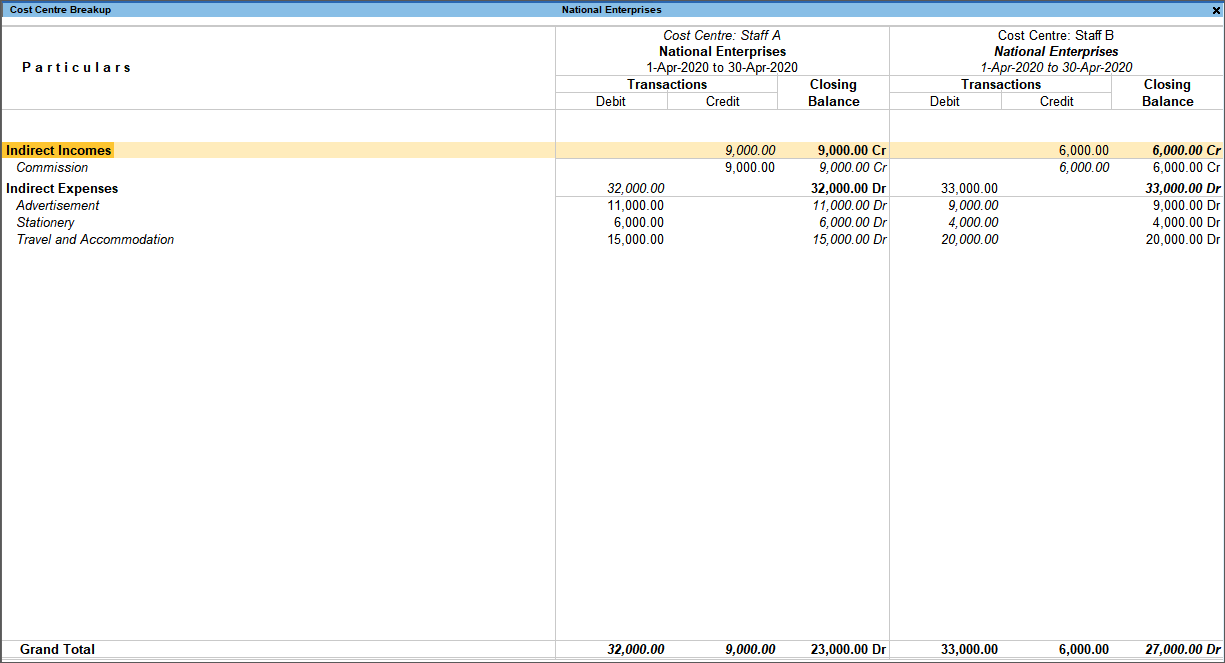
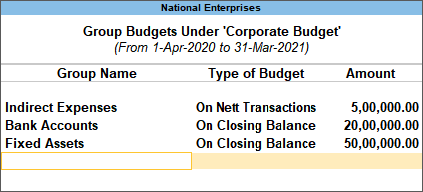
Using TallyPrime’s cost centre management will help you stay on top of all the spending’s even on little expenses and make confident decision. What’s more? You can set budget and track the variance.
Read more:











