A business depends heavily on its inventory management, which determines how smoothly it operates and serves customers while saving costs. Effective stock level management prevents stockpiling, which increases holding expenses, and stock shortages, which lead to loss of sales. To ensure effectiveness, businesses use the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula as their essential inventory management tool.
The economic order quantity system shows businesses how to order the right quantity of products, controlling their inventory costs. Through EOQ, companies can use data as a basis for inventory choices to maximise supply chain operations and improve profitability. Companies use EOQ to lower their costs while making better inventory purchases to run their operations more efficiently.
What is EOQ (Economic Order Quantity)?
Economic order quantity is a formula used in cost accounting to calculate how much optimum inventory levels of a product should be maintained to prevent understocking and overstocking. EOQ balances two critical inventory costs:
- Ordering costs – Expenses incurred each time an order is placed. This includes administrative fees and supplier charges.
- Holding costs – Business expenses for safely keeping unsold items. This includes warehouse rental and product depreciation.
By using EOQ, businesses can achieve a balance between frequent ordering (leading to high ordering costs) and ordering in large quantities (leading to high holding costs).
The economic order quantity formula explained
The EOQ formula is expressed as:
Economic order quantity = Square root of [(2 x demand(D) x ordering cost(S) / carrying cost(H)]
Where:
D = Demand (units per year). It is the total number of units required annually. This is based on sales forecasts and market trends.
S = Ordering cost per order. It is the fixed cost incurred every time an order is placed, including administrative and delivery charges.
H = Holding cost per unit per year. This is the cost of storing one unit for a year, including warehousing, insurance, depreciation, and opportunity charges.
Each component plays a vital role in calculating the most economical order quantity.
| How to become more efficient in Inventory Management | How Re-order Level of Stock Helps Keep Your Company’s Financial Health Stable |
Why is EOQ important?
- Cost reduction: EOQ minimises total inventory costs by optimally balancing ordering and holding expenses. It prevents both over-purchasing and the costs associated with frequent reordering.
- Optimised supply chain: Maintaining the right inventory levels ensures a smooth supply chain. EOQ helps prevent both stockouts and overstocking, ensuring products are available when needed.
- Operational efficiency: By determining the ideal order quantity, EOQ reduces the frequency of orders and eliminates excess costs related to storage and order processing.
- Higher profitability: Efficient inventory management reduces waste and lowers overall expenses, allowing businesses to allocate funds to other critical areas, thereby boosting profit margins.
- Strategic decision-making: EOQ provides data-driven insights, helping businesses make informed purchasing decisions, plan better, and ensure uninterrupted operations.
- Reduced administrative workload: With fewer order cycles, the EOQ model lightens the administrative burden involved in procurement, improving overall workflow and resource management.
How to calculate EOQ?
Example 1: Retail business
Factors affecting EOQ
- Demand fluctuations: Seasonal variations and shifting consumer preferences can lead to unpredictable demand, making it difficult for EOQ to consistently determine optimal order quantities and inventory levels.
- Ordering costs: Changes in supplier pricing, transportation charges, or administrative expenses can alter ordering costs, thereby impacting the EOQ calculation and influencing inventory decisions.
- Holding costs: An increase in warehousing fees, insurance premiums, or depreciation rates raises the cost of holding inventory, which affects EOQ outcomes and inventory strategies.
- Lead time: Longer lead times from suppliers require businesses to maintain higher safety stock, potentially impacting EOQ by necessitating adjustments in order quantities.
- Bulk discounts: Volume-based discounts reduce per-unit costs, which can encourage businesses to increase order quantities, influencing EOQ calculations to capitalise on cost savings.
Regularly updating EOQ values based on these factors ensures accurate inventory planning.
EOQ limitations
- Static demand assumption: EOQ assumes constant demand, but in reality, demand can fluctuate due to seasonality, market trends, or external factors, limiting its accuracy for dynamic inventory management.
- Fixed costs assumption: The model assumes that ordering and holding costs are fixed, but in practice, these can fluctuate due to changes in supplier prices, storage fees, or market conditions.
- No consideration for stockouts: EOQ does not account for unexpected supply chain disruptions or sudden demand spikes, which can lead to stockouts, impacting the model’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
- Not for perishable goods: It may not be ideal for perishable goods, as it doesn’t account for product shelf life, requiring businesses to adopt alternative strategies for inventory management.
Leveraging TallyPrime to maintain optimum inventory levels
- Automated inventory tracking and stock alerts
- Accurate cost calculations for better financial planning
- Real-time inventory updates to prevent overstocking and stockouts
- Seamless supplier management and order processing
How can software help?
Data is at the root of calculating EOQ with the EOQ formula. Accounting software with inventory management capabilities ensures you have the right data at any time.TallyPrime, complete business management helps you manage optimum inventory level. The inventory control such as reorder level helps you get rid of risk arising from overstocking as well understocking.
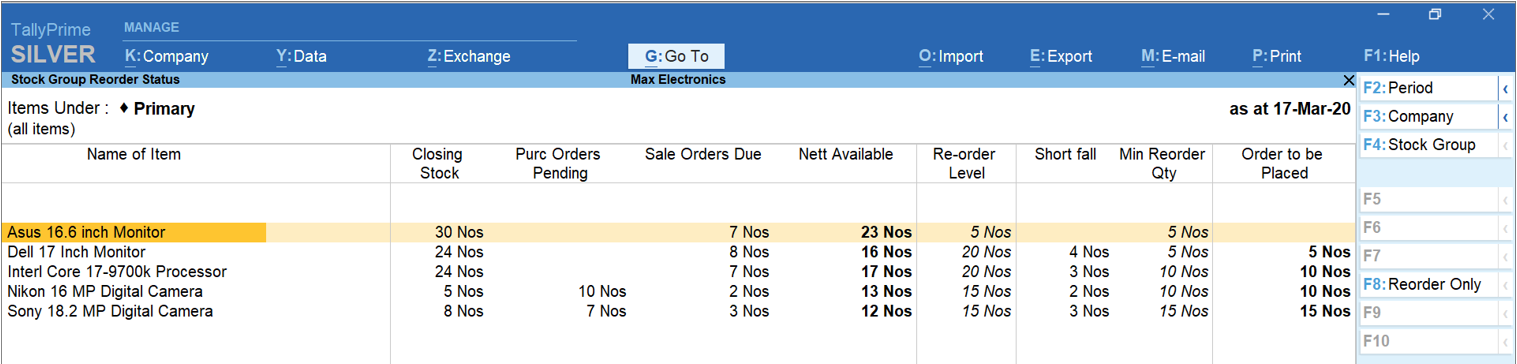
The re-order status report is quite helpful as it summarizes key information about your stocks, pending purchase orders, and more importantly, you will get to know the shortfall and the quantity of stock that needs to be replenished.
FAQs
1. What is EOQ and its formula?
Economic order quantity or EOQ is used in cost accounting to calculate how much optimum product inventory levels should be maintained to prevent understocking and overstocking. The formula is:
EOQ = sqrt(2 D S / H)
2. What are D, S, & H in EOQ?
The EOQ formula consists of three key components:
D (Demand): Annual quantity required
S (Ordering Cost): Cost incurred per order
H (Holding Cost): Cost of storing each unit annually
3. What are some of the assumptions to be kept in mind while calculating EOQ?
EOQ is based on the following assumptions:
Demand remains constant throughout the year.
Ordering and holding costs are fixed.
There are no stockouts or shortages.
4. How is EOQ different from MOQ?
The difference between EOQ and MOQ is:
EOQ (Economic Order Quantity): Determines the optimal order quantity to reduce costs.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The lowest quantity a supplier is willing to sell.
5. What are the objectives of EOQ?
The objectives of EOQ include:
Minimising total inventory-related costs.
Ensuring product availability without overstocking.
Optimising order frequency to improve cash flow.
6. What is an EOQ diagram?
The EOQ diagram provides a visual representation of the interconnection between ordering, holding, and total inventory expenses. The main objective is to determine the EOQ point that minimises total costs. The illustration demonstrates how multiple-order quantity levels affect total organisational costs.
Read more: