Access to finance remains a significant barrier for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) around the world. According to a World Bank report, about 40% of MSMEs in India cite access to finance as a major obstacle to their growth and development. Traditional banking systems often fail to meet the unique needs of these enterprises, leading to stringent credit checks, lengthy approval processes, and a lack of suitable financial products.
Given this backdrop, can there be a solution that offers MSMEs the financial support they need without the typical barriers?
Enter Decentralized Finance (DeFi) - a rapidly evolving ecosystem that leverages blockchain technology to create a decentralized, transparent, and accessible financial landscape. Small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) can access financing without the hassle of lengthy paperwork, stringent credit checks, or the need for collateral. Businesses can participate in global markets, manage their cash flow efficiently, and mitigate financial risks seamlessly. This is the promise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), a rapidly evolving ecosystem that is revolutionizing the way we think about financial services.
What is DeFI?
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is a financial ecosystem built on blockchain technology that operates without the need for traditional intermediaries like banks. Unlike the centralized financial systems, where intermediaries control access and facilitate transactions, DeFi operates on a peer-to-peer basis, using smart contracts to automate and execute transactions.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain. They are used to automate and execute financial transactions without the need for human intervention. Much like the vending machine that will only dispense your desired product after all requirements are met. If you don't select a product or insert enough money, the vending machine won't give out your product.
Defi vs traditional finance
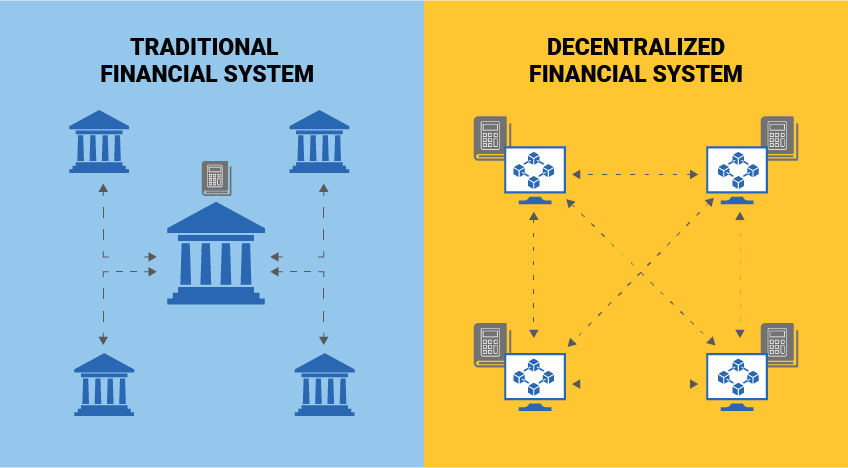
Traditional financial systems rely on a set of intermediaries such as banks, brokers, and exchanges connected by payment systems. These intermediaries serve as centralized actors that guard access to the financial system and provide customers with essential services such as record keeping, verification of transactions, settlement, liquidity, and security. They help with implementing regulatory goals such as tax reporting, anti-money-laundering laws, or consumer financial protection.
The intermediaries can hold significant power based on their preferential access to customers and data. This centralized position, if not properly harnessed and regulated, can lead to considerable inefficiencies, fragility, and systemic risk if core intermediaries become corrupted or investors lose trust in the system.
A decentralized financial system is not controlled by any central authority. It offers the possibility of a completely different financial architecture, commonly called decentralized finance (DeFi), where record keeping is decentralized, access to the system is anonymous and unrestricted, and any form of intermediation would be built on top of it. Instead, it is governed by a network of computers in a distributed ledger (blockchain) that runs smart contracts.
How does DeFi work?
DeFi applications and protocols are built on top of blockchains, such as Ethereum and Polygon. Blockchains are distributed ledgers that record all transactions in a tamper-proof manner. This makes them ideal for financial applications, as they provide a secure and transparent way to track and execute transactions.
The protocol layer supplies standards for specific use cases such as decentralized exchanges, debt markets, derivatives, and on-chain asset management. These standards are usually implemented as a set of smart contracts and can be accessed by any user (or DeFi application). To use DeFi, users need to connect their cryptocurrency wallets to DeFi applications or protocols.
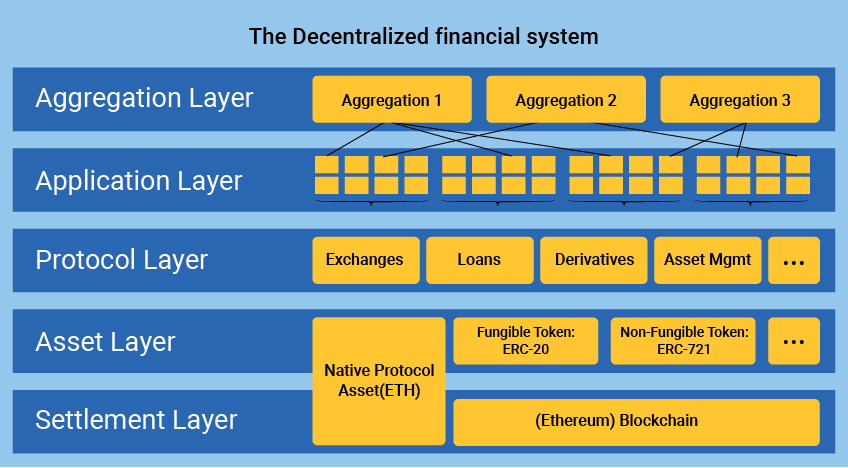
Once connected, they can access a wide range of financial services, including:
- Stablecoins: Digital money that seek to maintain a constant value of a token relative to some asset, most commonly the U.S. dollar or other major fiat currency.
- Exchanges: Allow users to trade one digital asset for another. DeFi exchanges avoid taking custody of user assets, either through a decentralized order book or by matching orders and setting prices algorithmically.
- Credit: Involves the creation of time-limited interest-bearing instruments, which must be repaid at maturity, and the matching of lenders and borrowers to issue those instruments.
- Derivatives: These are synthetic financial instruments whose value is based on a function of an underlying asset or group of assets. Common examples are futures and options, which reference the value of an asset at some time in the future.
- Insurance: Provides protection against risks by trading the payment of a guaranteed small premium for the possibility of collecting a large payout in the event of a covered scenario.
- Asset Management: Seeks to maximize the value of an asset portfolio based on risk preferences, time horizons, diversification, or other conditions.
Benefits and challenges of DeFi:
DeFi offers several benefits over traditional financial systems, including:
- Accessibility: DeFi is open to anyone with a cryptocurrency wallet. There are no KYC/AML requirements or credit checks needed to access DeFi services.
- Transparency: All transactions on DeFi applications and protocols are recorded on the blockchain, making them transparent and auditable.
- Efficiency: DeFi applications and protocols are automated and efficient, which means that users can access financial services quickly and easily.
- Innovation: DeFi is a rapidly growing ecosystem, with new applications and protocols being developed all the time. This means that users have access to a wide range of innovative financial products and services.
- Reduced Costs: DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs. This can enable more cost-effective financial solutions for users.
- Global Reach: DeFi operates on a global scale, without borders or restrictions. It can potentially reach users from all corners of the world, offering a unique opportunity for growth and market expansion.
While DeFi offers several benefits, there are also some challenges that need to be addressed, including:
- Complexity: DeFi can be complex for new users to understand. There are several different DeFi applications and protocols available, each with its own unique features and functionality.
- Security: DeFi protocols are vulnerable to hacks because they operate on open-source code, which can be exploited by malicious actors. Unlike traditional banks that have established security protocols and insurance mechanisms, DeFi is still in its early stages of development, making it more susceptible to vulnerabilities.
- Regulation: DeFi is a largely unregulated industry. This means that there is no government protection for users if they lose money due to a hack or exploit.
- User Education: DeFi can be complex for new users. Developing user-friendly interfaces and providing educational resources is essential to attract and retain users.
DeFi and MSMEs
With the help of the community and without the need to turn to a bank or non-banking financial company, MSMEs can meet their capital requirements thanks to decentralized community finance. Generating demand in advance guarantees MSMEs that lenders will visit their establishments. Less bureaucracy results in fewer loan defaults because MSMEs are now businesses that people often deal with directly.
According to a 2021, WEF report on Decentralised Finance, some businesses use payment companies like BitPesa in Africa, Tranglo in ASEAN and the major DeFi exchanges to either make direct payments or convert payment amounts to USD-backed stablecoin for cross-border remittance.
BitPesa in Africa, drastically reduced transaction costs for cross-border payments with DeFi. With approximately 6,000 users, in 2017 Bitpesa has generated an estimated $10,000,000 in trade volume per month in 4 of the 7 countries it currently operates. By using DeFi, BitPesa has decreased transaction costs by up to 75%, enabling more businesses to engage in international trade.
Opportunities for MSMEs
In both Indian and international markets, DeFi (Decentralized Finance) offers a transformative opportunity for MSMEs by providing access to financial services that are typically difficult to obtain through traditional banking channels:
- Access to Credit: DeFi platforms offer quicker and more accessible loans, helping to overcome the significant challenges of stringent requirements and lengthy approval processes in traditional banking. This effectively bridges the financing gap highlighted by the World Bank.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi significantly reduces the cost of financial transactions, which is vital for budget-conscious MSMEs.
- Improved Cash Flow Management: Through decentralized lending and borrowing platforms, MSMEs can better manage their cash flow, enhancing liquidity and supporting sustainable growth, as emphasized by the World Economic Forum.
- Global Market Participation for Indian MSMEs: DeFi enables Indian MSMEs to connect with international investors and customers, facilitating global market participation without extensive regulatory barriers.
- Streamlined Cross-Border Transactions for Global MSMEs: DeFi simplifies cross-border transactions, reducing costs and complexity, which is especially beneficial for MSMEs involved in export and import activities. The World Bank highlights that reducing cross-border payment costs can significantly boost global trade for MSMEs.
- Diverse Financing and Risk Management: DeFi offers a range of financing options and innovative risk management solutions, such as decentralized insurance and derivatives markets, helping MSMEs protect against market volatility.
- Decentralized Marketplaces: MSMEs can leverage decentralized marketplaces to reach a wider audience, conduct secure and transparent transactions, and strengthen their resilience and growth across different markets.
Indian MSMEs: Leveraging DeFi in 2024
Indian MSMEs should begin by educating themselves about DeFi (Decentralized Finance) and its potential benefits. Partnering with fintech companies or consultants who specialize in DeFi can provide tailored guidance and help MSMEs navigate the complexities of this emerging field. In 2024, MSMEs should take the following steps to access DeFi:
- Establish a Digital Wallet: Set up a secure digital wallet that supports DeFi transactions.
- Understand Regulatory Frameworks: Stay updated on the regulatory environment in India concerning cryptocurrency and DeFi to ensure compliance.
- Start Small: Begin by experimenting with small transactions or investments in DeFi platforms to understand the risks and benefits.
- Collaborate with DeFi Platforms: Partner with reputable DeFi platforms that offer services tailored for businesses, such as decentralized lending, payments, and asset management.
- Educate and Train: Invest in training for key personnel to ensure they understand how to use DeFi tools effectively and safely.
By taking these steps, Indian MSMEs can start integrating DeFi into their operations, gaining access to new financial opportunities and positioning themselves at the forefront of financial innovation.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is bringing intriguing options and transforming the financial sector, utilizing its advantages, such as financial inclusion, global reach, lower costs, and improved security. For MSMEs, both in India and internationally, DeFi can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and financial stability. However, to ensure the success and sustainability of DeFi solutions, it is crucial to address regulatory hurdles, security issues, and user education. Adopting DeFi means shaping the direction of finance itself, not just remaining current.

















