This article has been updated with the GST Council's decision that suppliers of goods need not pay tax on advance received with effect from 15th November, '17.
Receiving advance for an order is a common business occurrence. Suppliers usually ask customers to pay advance for an order as it serves as a commitment to not cancel the order. For persons registered under Excise and VAT, advances received were insignificant from a tax point of view. The liability to pay tax on a transaction arose at the time of removal of the goods or sale of goods under Excise and VAT, respectively.
Service suppliers are familiar with this rule in the Service Tax regime, where they are liable to pay tax on advances received.
Note that with effect from 15th November, '17, persons supplying goods are not required to pay GST on advances received from customers.
Here, we will guide you on how to effectively treat advance receipts under GST.
Which document is to be issued when receiving an advance?
On receiving an advance for an order, a supplier should issue a Receipt Voucher to the person paying the advance. It is important to note that the supplier is liable to pay tax on the advance received under GST. Hence, the tax applicable on the advance amount should be shown in the receipt voucher. Tax should be calculated at the rate applicable to the goods and/or services for which the advance is received. Based on whether the recipient is intrastate or interstate, the tax charged will be CGST + SGST (intrastate) or IGST (interstate).
Important details to be captured in a advance receipt voucher under GST
- Supplier’s name, address and GSTIN
- Serial number of the receipt voucher, not exceeding 16 characters, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters hyphen (-) or slash (/). It must be unique for a financial year
- Date of issue
- If the recipient is registered, the recipient’s name, address and GSTIN or UID
- Description of the goods or services
- Amount of advance taken
- Rate of tax (CGST, SGST, IGST, UTGST or Cess)
- Amount of tax (CGST, SGST, IGST, UTGST or Cess)
- If the supply is interstate, the place of supply, along with the state name and the state code
- Whether tax is payable on reverse charge
- Signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative
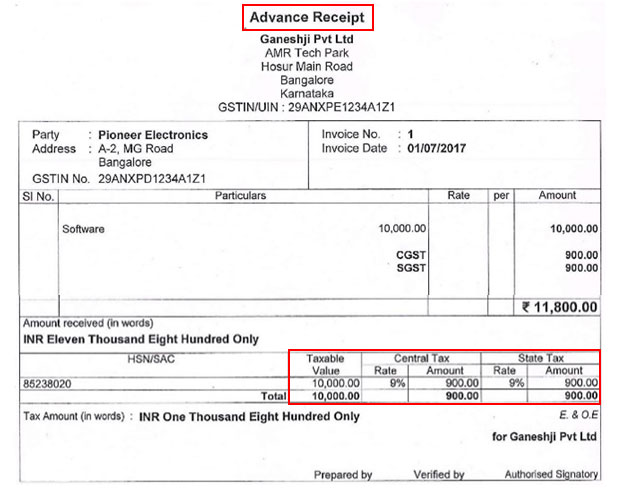
Example: Ganeshji Pvt. Ltd. in Bangalore receives advance of Rs. 10,000 (excluding tax) from Pioneer Electronics in Bangalore for an order of 2 Software. On this advance of Rs. 10,000, Ganeshji Pvt. Ltd. should charge tax @ 18%, which is the GST rate applicable to software. Since Pioneer Electronics is located in Bangalore, the taxes to be charged are CGST + SGST.
The advance receipt voucher issued by Ganeshji Pvt. Ltd. will appear as shown below:
What to do if the rate of tax cannot be determined at the time of receiving advance?
If the rate of tax cannot be determined at the time you receive an advance, you should pay tax @ 18%
What to do if you cannot determine whether the supply is interstate or intrastate at the time of receiving the advance?
In this case, the supply should be treated as an interstate supply.
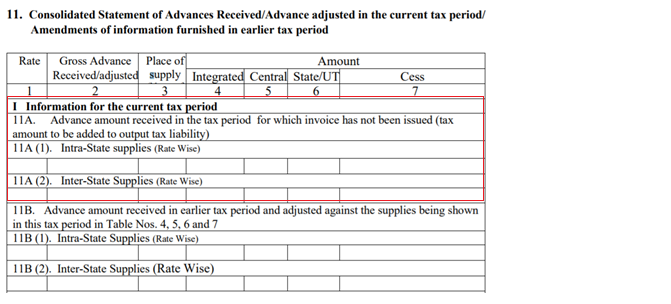
How to furnish details of advances received under GST?
Details of advances received for which invoice has not been issued in the month should be furnished in Form GSTR-1: