- Understanding Debit and Credit just got Easier
- Golden Rules of Accounting
- Example of the Golden Rules of Accounting
Understanding Debit and Credit just got Easier
Got stuck in figuring what to Debit and Credit? Yes, like some of you, even I used to get puzzled as well in my early days. By the time I would settle my understanding on golden rules of accounting: debit and credit, one or the other scenarios would again lead me back to zero and start my understanding afresh.
After following some of logics below, I settled my understanding on debit and credit and after that, I got it right every time. Let’s clear the confusion once and for all!
Instead of beginning with golden rules of accounting, let me register debit and credit as shown in the table.
|
Debit |
Credit |
|
Positive (+) |
Negative (-) |
|
Come |
Go |
|
Receive |
Give |
|
Receiver |
Giver |
|
Deposit |
Withdraw |
|
Increasing |
Decreasing |
From the above table, it’s clear that it is neither a theory nor a puzzling topic anymore - it’s just logic and reasoning. To summarize - Debit is all about incoming/deposits and Credit is all about outgoing/withdrawal.
For example, you purchased a computer by paying 25,000 by cash. Here, you are receiving a computer so it should be debited, and cash should be credited since it is going out.
Voila! You just recorded an accounting transaction even without looking at the golden rules of accounting.
Golden Rules of Accounting
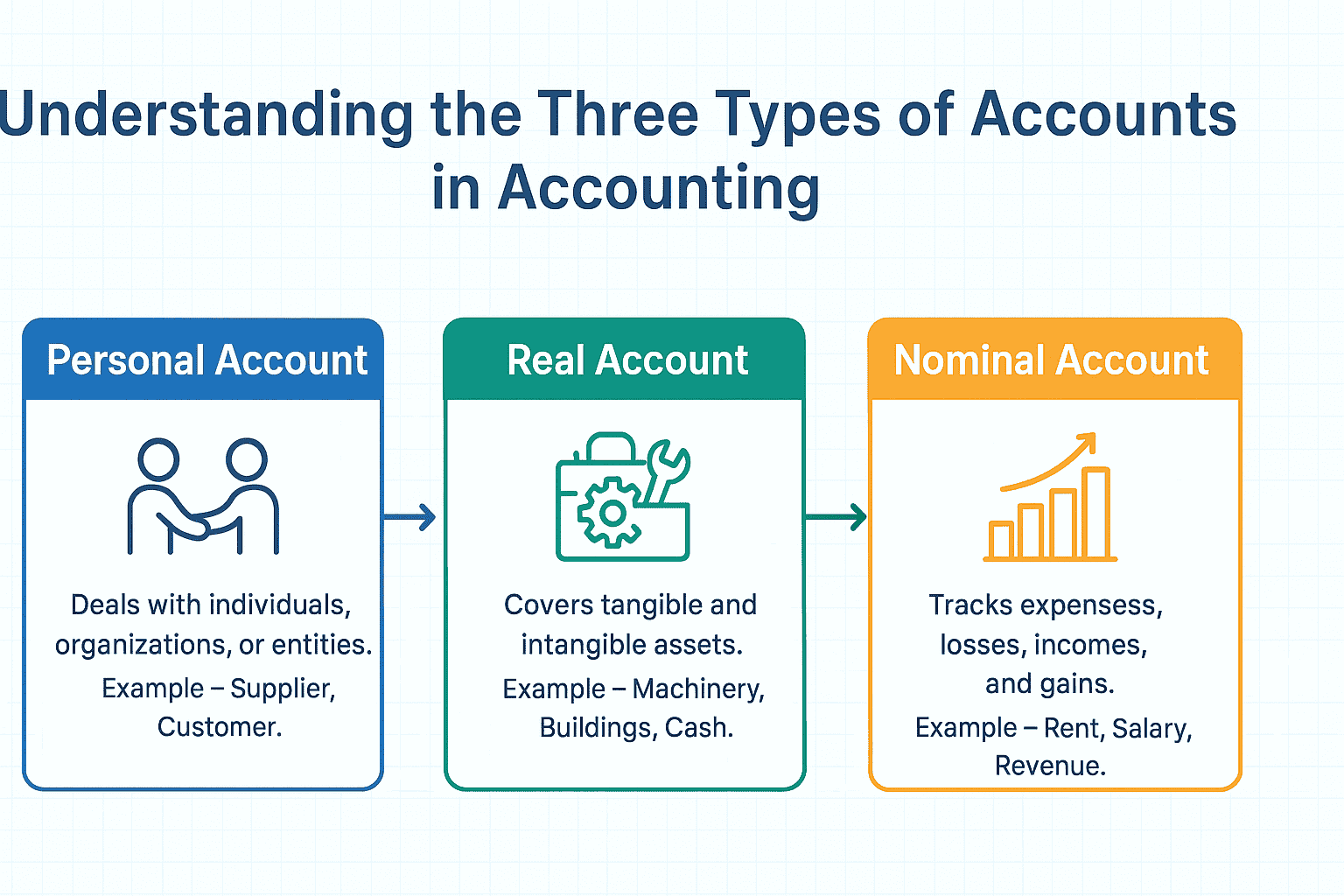
With the above understanding, let us introduce the golden rules of accounting. Golden rules of accounting refer to a set of pre-defined principles which guides the sequential way of recording the transactions using double entry system of bookkeeping. In this system, every transaction involves both a debit and a credit entry, and the rules are categorized based on the three types of accounts: Personal Account, Real Account, and Nominal Account.
Types of Accounts
For all those who are still curious to know the definition of a real account, personal account and nominal account, here is the brief about it.
Real Account
Rule: Debit the receiver, Credit the giver
Real accounts are those accounts which are related to assets or properties or possessions. It includes both tangible and intangible. When dealing with individuals, organizations, or entities, the person or entity receiving something is debited, and the person or entity giving something is credited.
Personal Account
Rule: Debit what comes in, Credit what goes out
Real accounts deal with tangible and intangible assets (e.g., cash, machinery, buildings, patents). When an asset comes into the business, it is debited, and when an asset goes out, it is credited. This includes all accounts related persons consist of natural, artificial and representative accounts.
Nominal Account
Rule: Debit all expenses and losses, Credit all incomes and gains
Nominal accounts deal with expenses, incomes, losses, and gains. Expenses and losses are debited, while incomes and gains are credited.
let's have a look how these rules will help businesses in smooth transaction.
What are the three golden accounting rules?
The three golden rules of accounting apply to different types of accounts, let's understand them with examples
Debit the receiver and credit the giver
This golden rule applies to the personal account. When the business receives something, then the account must be debited and when the business gives something then the account must be credited as per this rule of accounting.
Suppose you pay ₹41,500 to a supplier. The supplier is the receiver (they are getting paid), and cash is going out from your business (giver).
| Date | Particulars | Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-012025 | Supplier’s Account | 41,500 | - |
| To Cash Account | - | 41,500 | |
| (Being payment made to supplier) |
Debit what comes in and credit what goes out
This golden rule applies to real accounts (also known as permanent accounts). Examples of real accounts include equity, asset, and liability accounts. When the business is acquiring something such as an asset, then the account of the business has to be debited. On the other hand, when the business is giving something out then the account will be credited.
You purchase machinery worth ₹8,30,000 in cash. Machinery is what comes in, and cash is what goes out.
| Date | Particulars | Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10-01-2025 | Machinery Account | 8,30,000 | - |
| To Cash Account | - | 8,30,000 | |
| (Being machinery purchased for cash) |
Debit expenses and losses, credit income and gains
This golden rule applies to nominal accounts (also known as temporary accounts). Examples of nominal accounts include expense, gain, loss, and revenue accounts. As per the rule, when the business incurs a loss or has an expense then you need to debit the account. If the business has a gain or earns an income then the account should have a credit.
Now you earn revenue of ₹83,000 in cash. Cash is coming in (asset increase), and revenue is income being credited.
| Date | Particulars | Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20-01-2025 | Cash Account | 83,000 | - |
| To Revenue Account | - | 83,000 | |
| (Being revenue earned in cash) |
What are modern rules of accounting?
The modern rules of accounting have six types of accounts rather than the three types of accounts in the traditional rules of accounting. As per the modern rules, the six accounts are an asset, capital, drawings, revenue, liability, and expense.
You have to debit the increase while you credit the decrease for the asset account. For liability, you credit the increase and debit the decrease. You debit the decrease and credit the increase for a capital account. For the revenue account, you debit the decrease and credit the increase. For the drawings account, you debit the increase and you credit the decrease. You debit the increase and you credit the decrease for the expense account.
Why the Golden Rules of Accounting Matter – Key Benefits Explained
The golden rules of accounting aren’t just textbook definitions—they’re the backbone of trustworthy financial management. By following these simple but powerful rules—debit the receiver, credit the giver; debit what comes in, credit what goes out; and debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains—businesses can keep their financial records accurate, transparent, and easy to manage.
Here’s why these rules are so essential and the major benefits they bring:
1. Spotting Errors Becomes Easier
The double-entry system, guided by the golden rules, makes it hard to overlook mistakes. Every debit entry has a matching credit entry, so the books always need to balance. If they don’t, it’s a clear sign something’s off. This helps businesses quickly identify and fix errors like missing transactions, number typos, or wrong entries—making financial reports more reliable.
2. Audit-Ready Records with Less Hassle
A well-maintained accounting system is easier to audit. Whether it’s an internal review or an external audit, following the golden rules ensures that records are structured, consistent, and easy to trace. Auditors can quickly follow the money, reducing the time and effort needed to verify transactions. Plus, clear books reflect strong financial discipline, which builds trust and can even lower audit costs.
3. Aligns with GAAP Standards
The golden rules form the practical steps for applying Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), the global standard for financial reporting. By categorizing transactions correctly and following debit/credit guidelines, businesses ensure their records meet GAAP’s expectations for recognizing income, tracking expenses, and showing financial health. This makes reports more credible to investors, banks, and regulatory bodies.
4. Creates Consistency and Easier Comparisons
Accounting works best when it’s consistent. These rules give businesses a uniform approach to recording transactions, which helps track progress over time. It’s also easier to compare performance across companies because everyone’s following the same method. Whether you’re an investor or a financial analyst, this consistency provides clarity and confidence in the data.
FAQ:
Why is the receiver debited and the giver credited?
Let us say that a business called A sells an asset to another business called Z. The business Z has received the asset but is yet to pay. The asset has been sent from A at this point although A has not received the payment from Z yet. The receiver is debited because he is going to pay business A eventually while business A is credited because it will receive the payment from Z in due time.
Which accounting standard is applicable as per Section 133, of the Companies Act, 2013?
According to section 133 of the Companies Act, 2013, the Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) are applicable. It states that these accounting standards have been developed according to the Indian environment, both legal and economic. Eventually, the Ind AS will align with IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) meaning it will follow its lead either partially or fully.
What are the 3 types of accounts?
The three different types of accounts in accounting are Real, Personal and Nominal Account.
Why Use the Golden Rules of Accounting?
The golden rules of accounting help record transactions accurately, consistently, and clearly. They prevent errors, ensure reports are easy to understand and compare, and keep your business compliant with standards like GAAP. Plus, they create a clear audit trail, making it easier to track and verify financial activities.
How Do They Work with Double-Entry Bookkeeping?
Double-entry bookkeeping records every transaction in two accounts to keep the equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity balanced. The golden rules guide you on which account to debit and which to credit, making it easy to apply this system and keep your books accurate and balanced.
Read More on Accounting
Accounting Software, Accounting Equation, Accounting Principle, Accounting Methods, Accounting Rate of Return, Cash Accounting, Accrual Basis of Accounting, Financial Accounting, Cost Accounting, Accounting Standard, Cash Accounting vs Accrual Accounting, Cost vs Management Accounting











