- What is a T Account?
- Why Do Accountants Use T Accounts?
- T Account Example
- What Are the Problems with T Accounts?
- Why Can't Single Entry Systems Use T Accounts?
- Easy T Accounts For Small Businesses
Bookkeeping is the process by which a company’s financial transactions are recorded and organized. There are two basic types of bookkeeping. Single-entry bookkeeping and double-entry bookkeeping. Single entry bookkeeping is the simplest form of bookkeeping where a single entry is made for every transaction usually in a cash book.
Double-entry bookkeeping is based on the principle that every transaction affects a minimum of two accounts. Transactions are recorded as debits and credits. In this system, the total credits must always equal the total debits. This is a more robust form of accounting that double-checks each transaction and leaves scope for different aspects of business transactions such as buying and selling on credit. A T account is an informal term that refers to financial records that use double-entry bookkeeping.
What is a T Account?
A T account is the visual representation of accounts in the form of the alphabet T. A large T is drawn on the page. The name of the account is written above the T. The left side of the T is always used to record the debit transactions while the right side records the credit transactions. The debits and credits are separated by the vertical line of the T. This makes it visually easier to track the debits and credits or in other words the additions and subtractions to each account. Another name for a T account is a ledger account.
For asset accounts, the debit (left) side always indicates an increase to the account and the credit (right) side indicates a decrease to the account. Examples of asset accounts are cash, inventory, and account receivable. For liabilities and equity accounts, the debits indicate a decrease to the account and a credit indicates an increase to the account.
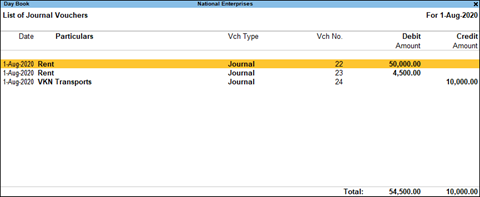
T Account Example: Tally Cash Book Screen Showing Debit and Credit Columns
Why Do Accountants Use T Accounts?
T accounts make it easier to manage a double-entry bookkeeping system. They help record each transaction with its corresponding entry in a different account. This literally means that there is a double entry, i.e., two aspects for each transaction in the system. So, the total debits must always balance the total credits to balance the books. If there is a difference, it means that an error has been made.
Having the simple T account structure makes it very easy for the person who is recording the transaction to make two corresponding entries in the books. It makes the recorded information easier to understand at a glance. This system is used by accountants or CPAs (Certified Public Accountants) and it is a good practice for all businesses that use double-entry bookkeeping to use the T account structure in their general ledger.
The advantages of a T account system are:
- It maintains the record of both personal and impersonal accounts
- The books are arithmetically balanced
- It is easy to detect errors and minimize frauds
- It is easy to see outstanding balances
- It is easy to view the financial position of the business for a time period and compare it with another time period
- It is easy to determine taxes based on the net earnings of the business
- It is easy to view the financial position of the business and make appropriate decisions.
T Account Example
|
|
|
ABC Company |
Assets |
|
|
|
|
Debits |
|
|
Credits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22/07/2021 |
Cash |
$ 200 |
22/07/2021 |
Inventory |
$200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In the T account example above, we have recorded the sale of an item that is worth $200 from ABC Company. The company has received $200 cash and the inventory account loses 200$ worth of an item. This T account example simply illustrates how the balancing of a ledger works.
In simple words
- The left column of debits increases an asset or expense account
- The right column of credits decreases an asset or expense account
- The left column of debits decreases liability, revenue, or equity accounts
- The right column of credits increases liability, revenue, or equity accounts.
What Are the Problems with T Accounts?
Most of the problems with T accounts creep in with errors on the part of the person recording the transaction. Some may be numerical while others are accounting principle errors.
-
Errors Of Principle
This happens when the basic principles of double-entry accounting and T accounts are not followed correctly. This could be a simple incorrect column error or an accounting principle error. One T account example is; when something is purchased for the company, it could either be categorized as an expense or as a capital cost. The correct categorization is at the discretion of the accountant who is making the entry. This would normally be identified only during the audit and not by the T account system as it does not affect the balance of the books. It can cause incorrect reports and statements about the finances.
-
Recording Error
There are two types of recording errors. One is when the accountant forgets to make an entry for a transaction altogether and does not enter it into the books. Such an error will not show up in T account systems as it does not affect the way the books balance. Another error is the incorrect recording of the transaction on the wrong side of the T or mistyping the numbers. This can be easily corrected if the accountant checks the books after every entry.
-
Time Consuming And Costly
Manually maintaining a T account system is time-intensive and expensive. It would require dedicated manpower just for the data entry. However, it is a mandatory system of accounting required by governments and financial institutions. It is, however, very easy, efficient, and cost-effective to use accounting software solutions such as TallyPrime to implement T account bookkeeping in a business.
Why Can't Single Entry Systems Use T Accounts?
Single-entry bookkeeping cannot use T accounting simply because the system does not differentiate between debits and credits. The T account system is based on the principle of classifying each transaction as debit and credit to different ledgers or books.
Easy T Accounts For Small Businesses
TallyPrime makes maintaining a double-entry accounting system easy and stress-free. It is easy for the accountants to record transactions without any errors. Tally also makes it effortless to extract the reports and trial balances that would be required for auditing. With TallyPrime, you just need to record your organization’s day-to-day transactions, and you get insightful business reports, including the T accounts (commonly known as general ledger accounts) are auto-generated. These reports come in handy especially when you try to get financers to invest in your business, as they get a complete view of your business’ financial status.
Learn how to view and analyse accounting reports in TallyPrime right here!
Book a free demo with us today, to take care of your everyday accounting needs, seamlessly!
Explore more Products
Best Accounting Software in USA, Accounting Software for Small Businesses in USA, Factors to Consider before Buying Bookkeeping Software in USA, Benefits of Payroll Management Software for Small Businesses in USA, Invoicing & Billing Software in USA That Best Suits Your Business
Read more on Accounting
COGS vs Expenses, What is Revenue Recognition?, Financial Accounting Vs. Managerial Accounting, Real Estate Accounting in US Best Practices and Bonus Tips, Difference Between an Estimate, Quote, Bid, and Proposal, How to Easily Build Great Estimates for Your Projects?
Popular Articles
Differences Between Trial Balance & Balance Sheet, What is the NOPAT Formula?, What is A Pay Stub?, What is a credit note?, How to Find Gross Profit?, What are Operating Expenses?, Break Even Point Formula, What is the Gross Margin Formula?, What is the Direct Write Off Method?, What Is Interest Expense?










