- What is gross profit?
- What is the formula for gross profit?
- How to calculate gross profit margin?
- What's the difference between net and gross profit?
- Keep a sharp eye on your costs as well as profitability!
As a business owner, one of the most important factors that you will have to monitor is the profit that your company is making. Profit is the money that you make through your business activities. It is the aim of every business that their profit should grow over a period of time. So, to know the health and success of your business it is important that you should know how to assess profitability. There are two types of profitability that you can monitor for a business; gross profit and net profit.
What is gross profit?
The manufacturing or production of the goods that the business sells involves a cost which is referred to as the cost of goods sold (COGS). The difference between the total sales revenue that you make and the COGS that you have spent is the gross profit of your business. It must be noted that ‘total’ sales refer only to the sale of the goods that have been manufactured and not the sale of any of the assets such as equipment or buildings.
| What is the NOPAT Formula? - Net Operating Profit After Tax | What is the Gross Margin Formula - How to Calculate? |
What is the formula for gross profit?
The gross profit formula is the difference between the total sales revenue and the COGS.
The gross profit formula is:
Gross Profit = Total Sales Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold
In this gross profit formula, the total sales revenue is the money that the business has made by selling its goods in the specified time period. There are no deductions made from this total sales revenue. The COGS or Cost Of Goods Sold is the direct cost that has been incurred to produce the goods. This cost includes labor, facility overheads, materials, storage, and depreciation. It is not inclusive of marketing or administrative charges incurred.
As an example, let us calculate the gross profit for a company that has been making paper cups. We are to calculate the gross profit that the company has made for the financial year. We first calculate the total sales revenue of the company through the sale of the paper cups for the year and find it to be $30,000. The cost of producing the paper cups including materials, labor, overheads, and storage for the same time period is $15,000. So, we use the gross profit formula which is:
Gross Profit = Total Sales Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold
Total Sales Revenue= $30,000
Cost of Goods Sold= $15,000
Gross Profit = $30,000 – $15,000= $15,000
So, the gross profit of the company is $15,000 for the financial year
How to calculate gross profit margin?
Gross profit margin is another metric that is important to express the profitability of the company. It is expressed as a percentage. Gross profit margin is also referred to as the gross profit
The formula for Gross Profit Margin is :
Gross Profit Margin = [(Total Sales Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold)/Total Sales Revenue] x 100
For the paper cup company example we calculate the gross profit margin as follows :
Total Sales Revenue= $30,000
Cost of Goods Sold= $15,000
Gross Profit Margin = [(Total Sales Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold)/Total Sales Revenue] x 100
Gross Profit Margin = ($30,000 - $15,000)/$30,000 x 100 = 50%
So, we can say that fifty percent of the total sales revenue remains after deducting the cost of goods sold.
Why is gross profit important?
The ultimate goal of every business is to be profitable and make money from their manufacturing. In order to be profitable, the company must be able to sell its goods for an amount that is more than the cost incurred producing them. In accounting terms, this is the gross profit.
If the gross profit and therefore the gross profit margins are falling, it implies that the company is becoming less profitable. A falling profit margin tells the management that they have to control the cost of producing goods sold to increase the gross profit margin. The organization may have to relook its purchasing policy and renegotiate its pricing. They may also have to contain their overheads and trim labor costs or improve efficiency.
On the other hand, a falling gross profit could indicate that you are selling your goods at a price that is far too low for the company to make enough profits. So, the management might have to tweak their pricing to be more profitable.
What's the difference between net and gross profit?
|
Gross Profit |
Net Profit |
|
Definition |
|
|
The gross profit is the difference between the total sales revenue and the cost of producing the goods sold. In other words, it is the amount of income that remains after you have paid for all the direct costs and expenses related to making the product. This cost of producing the goods includes labor, facility overheads, materials, storage, and depreciation but does not include marketing, administrative charges, and other amounts that the company has to payout.
|
Net profit is the amount that remains after the company has paid not only for the cost of producing goods but also for interest, taxes, and other operating costs over the given period of time. When this amount is negative it is called the net loss and not the net profit.
|
|
Formula |
|
|
Gross Profit = Total Sales Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold
Only includes the costs that are directly related to the production of the goods |
Net profit = Gross profit – Expenses
Also includes the other fixed expenses that the company has to bear such as interest, salaries, administrative costs, etc. |
|
Objective |
|
|
To determine the difference between costs and revenue, i.e., profitability |
To determine performance |
|
Application |
|
|
Control costs and determine the right pricing |
Study the company’s overall performance |
|
Reliability |
|
|
Can be used to determine and control production costs but cannot be used for overall financial decision making |
Is vital to make management decisions considering the overall financial health of the company |
|
Credit Balance |
|
|
Is the credit balance of the trading account |
Is the credit balance of the overall profit and loss account |
The biggest difference between gross profit and net profit is that net profit also includes the other expenses that the company incurs such as administrative, marketing, general, and non-operating expenses. These costs can be called the fixed costs as they do not vary much over time. They are also called indirect expenses. Some examples of these costs are marketing, advertising, depreciation, amortizations, dues, lease of equipment, interest on loans taken, insurance, taxes, rent, utilities, subscriptions, and salaries. The fixed or indirect expenses are some of the additional payouts that a business makes that are not directly related to the cost of producing the goods sold but are necessary to run the business. So, it is entirely possible that a company may make a gross profit, but after the payouts of fixed costs may make a net loss instead of a net profit.
So, the net profit of a company is a more accurate number to tell you how profitable your business is. A good net profit indicates that the company is in good health and is actually making money. It is an important number for investors and financial institutions to evaluate the financial health of the company. It tells you more clearly how much cash the company has left in hand after paying off all their dues and bills.
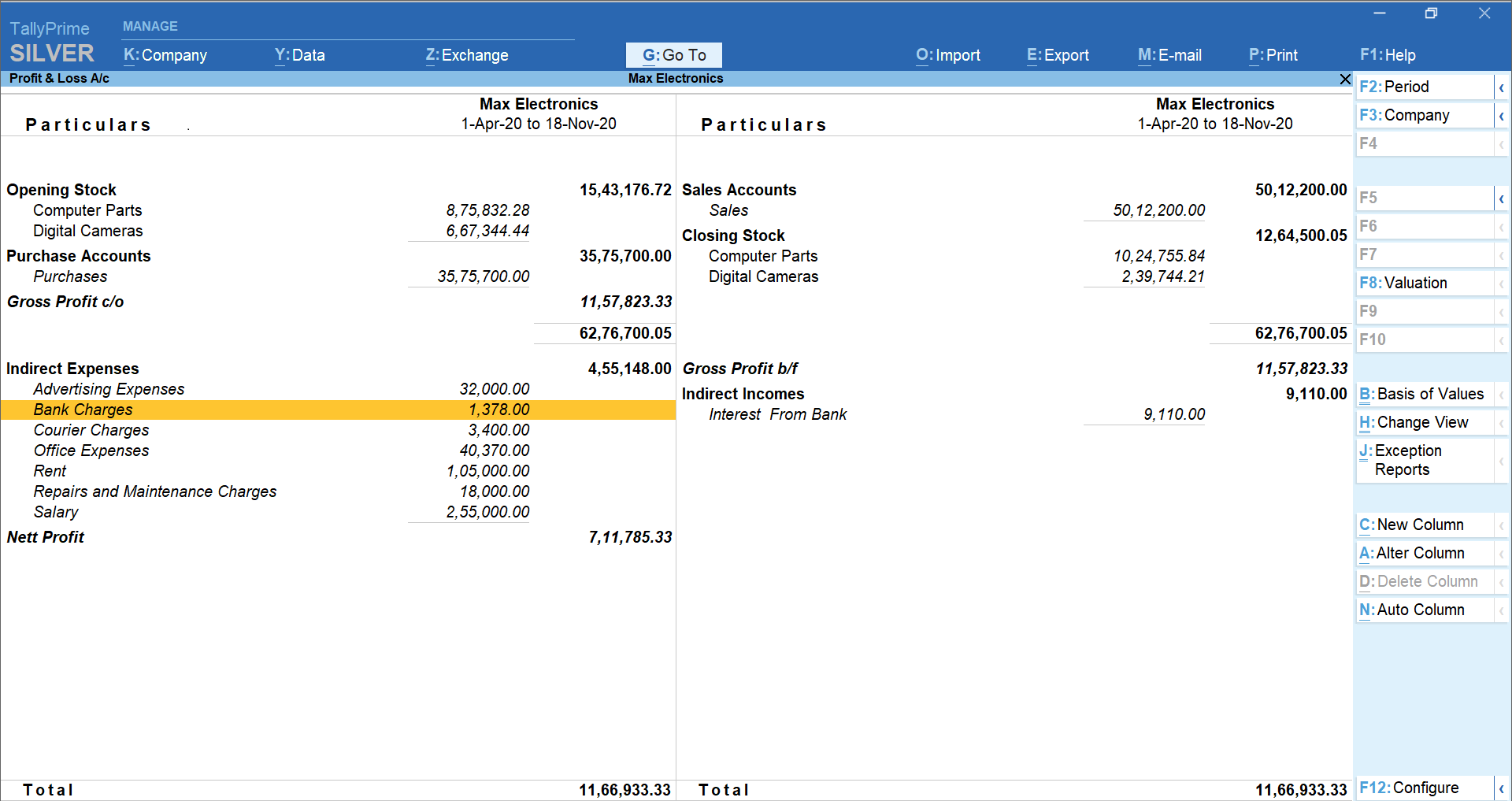
Gross profit and net profit on the profit & loss account report
Keep a sharp eye on your costs as well as profitability!
You need to calculate and keep both the gross profit and net profit as high as possible to ensure the financial success and health of your company. A good business management software such as TallyPrime does this for you effortlessly.
- Regardless of whether you are a large or small business, gross and net profit are two important numbers to calculate and monitor through your business management software
- TallyPrime makes it easy to calculate and track the gross profit to keep the costs of production as low as possible and to determine the ideal price for your goods
- You can generate stock item-wise gross profit that helps you track the products with a poor gross profit margin
- The comparative analysis reports such as monthly, quarterly or even on daily basis, help you keep a check on the trends
- The net profit is also generated by TallyPrime to get a bird’s eye view of the overall financial health of the company
Explore more Products
Best Accounting Software in USA, Accounting Software for Small Businesses in USA, Factors to Consider before Buying Bookkeeping Software for Your Business in USA, Benefits of Payroll Management Software for Small Businesses in USA, Invoicing And Billing Software in USA That Best Suits Your Business
Read more on Accounting
COGS vs Expenses, What is Revenue Recognition?, Financial Accounting Vs. Managerial Accounting, Real Estate Accounting in US Best Practices and Bonus Tips, Difference Between an Estimate, Quote, Bid, and Proposal, How to Easily Build Great Estimates for Your Projects?
Popular Articles
Differences Between Trial Balance & Balance Sheet, What is the NOPAT Formula?, What is A Pay Stub?, What Are T Accounts?, What is a credit note?, What are Operating Expenses?, Break Even Point Formula, What is the Gross Margin Formula?, What is the Direct Write Off Method?, What Is Interest Expense?










