The word tax evokes a look of dismay and misery for all companies. All those hours spent filling out forms, calculating taxes, and finally seeing a part of your earnings go to the government is painful. But what choice do you have? If you want to be a legal entity in India, you have got to pay corporate tax.
Corporate tax basics
Corporate tax is a tax on income paid by domestic and foreign companies that receive income from business activities conducted in India. The government of India has specified tax rates for companies that must be paid annually on their income.
You must first understand which tax slab you are under to understand the rate of tax you must pay per annum. The tax rates are published under the Income Tax Act of 1961, with occasional amendments.
Corporate tax rates
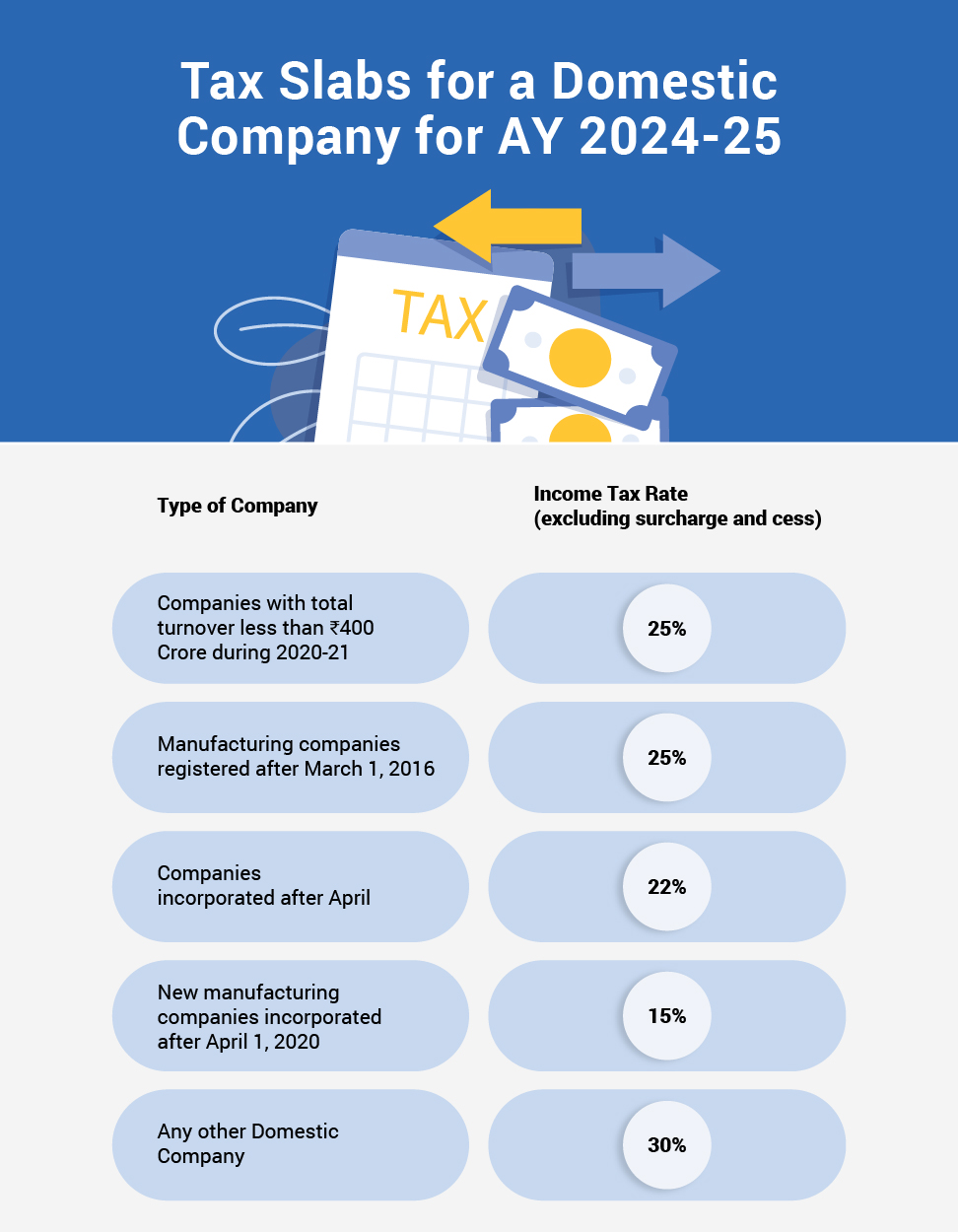
All domestic companies with a total turnover of ₹400 Crores or less during the previous year, 2020-21, must pay 25% tax. This is the standard tax rate for all business enterprises in India.
The tax authority has also given special consideration to certain companies and lowered their tax rates.
- Businesses engaged in the manufacturing of products and research and distribution of the said products must pay a tax of 25%. These businesses must be set up and registered after March 1, 2016, for this tax rate to be applicable.
- All companies incorporated on or after April 1, 2020, are liable to pay tax at the rate of 22%.
- All new manufacturing companies incorporated on or after April 1, 2020, will be charged at 15%.
- Companies incorporated on or after April 1, 2020, that are not engaged in manufacturing are charged at 22%.
These include:
There are tax deductions you can claim to reduce your tax liability. To have a look at tax deductions, have a look at our tax deductions guide.
Forms to fill
The tax authorities give different ITR forms. Knowing which ITR form applies to your business for ITR filing is important. Have a look at different ITR forms important for small businesses and identify which one applies to your enterprise:
|
Form |
Type of business |
|
ITR-3 |
For individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) with income from business or profession |
|
ITR-4 (Sugam) |
For small business owners who maintain a sales ledger instead of books of accounts |
|
ITR-5 |
LLPs/Partnerships |
|
ITR-6 |
All companies, excluding those claiming exemption under section 11 |
Now that we have covered which tax slab you fall under and the form you must fill out, let's discuss the critical timelines for ITR filing and the consequences of missing deadlines.
Deadlines for tax filing and penalties
The deadline for filing Income tax for Assessment Year 2024 – 25 is as follows:
- Businesses requiring audit - 31 October 2024
- Businesses that don’t require an audit – 31 July 2024
- Transactions under transfer pricing – 30 November 2024
If you miss ITR filing a late filing fee up to ₹5000 will be charged depending on the date of actual filing and the taxable income. If a tax refund is approved, it might get delayed if you miss the ITR filing last date. Also note that an additional interest charge will be levied on unpaid taxes.
This is a bird’s eye view on tax rates and laws applicable to businesses. There are conditions attached to every law and tax deductions you can claim. Be mindful of all the rates and deadlines so you can sharpen your pencils and get to tax filing well before the deadline.
Need help in calculating those long winding GST payments for your services and products. Use our GST calculator and get your GST calculations ready in seconds.










