VAT (Value Added Tax) invoices are vital documents for corporations in Saudi Arabia, detailing the VAT charged on income and paid on purchases. They encompass important statistics like dealer and customer data, invoice dates, and portions. Compliance with the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) regulations guarantees VAT invoices meet criminal requirements, facilitating accurate tax reporting and auditing. Failure to hassle compliant invoices can result in effects and tax audit complications.
VAT Invoices in Saudi Arabia: Main Requirements
Saudi Arabia has specified certain requirements for VAT invoices in implementing its e-invoicing under the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority, to promote tax compliance and to facilitate business processes. Below are the main requirements for VAT invoices by ZATCA regulations:
Key Requirements for VAT Invoices
- Each VAT invoice should contain the following details among others:
- Name and address of the seller as well as his VAT registration number.
- Buyer's name and address (for B2B).
- Date of issue and consecutive sequential invoice number.
- Description of goods or services supplied.
- Amount excluding VAT, the rate of VAT and the total amount including VAT.
- A QR code with relevant tax details (compulsory for B2C and for B2B for Phase 2)
VAT Invoice Types
VAT is classed into 3 most important sorts depending on the character of goods and services. These categories are very crucial for corporations to recognize so that you can observe the policies set by the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA). Here are the types of VAT:
Standard Rate (15%): The standard VAT rate is 15% for most goods and services sold in the Kingdom. It was hiked from 5% on July 1, 2020, through economic measures taken due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Common items in this category are:
- Food and drinks
- Local transportation services
- Most retail products and services
Zero-Rated Supplies (0%): Zero-rated supplies are taxable but charged at a rate of 0%. This means that while VAT is technically applicable, no tax is collected on these transactions. Businesses can reclaim input VAT on these supplies. Examples include:
- Exports of goods and services
- International transportation services
- Certain medical supplies and investment metals (e.g., gold, silver)
Exempt Supplies: Exempt supplies are not subject to VAT at all, meaning no VAT is charged, and businesses cannot reclaim input VAT on these transactions. Common exempt categories include:
- Residential real estate rental
- Financial services (e.g., loans, mortgages)
- Certain educational and healthcare services
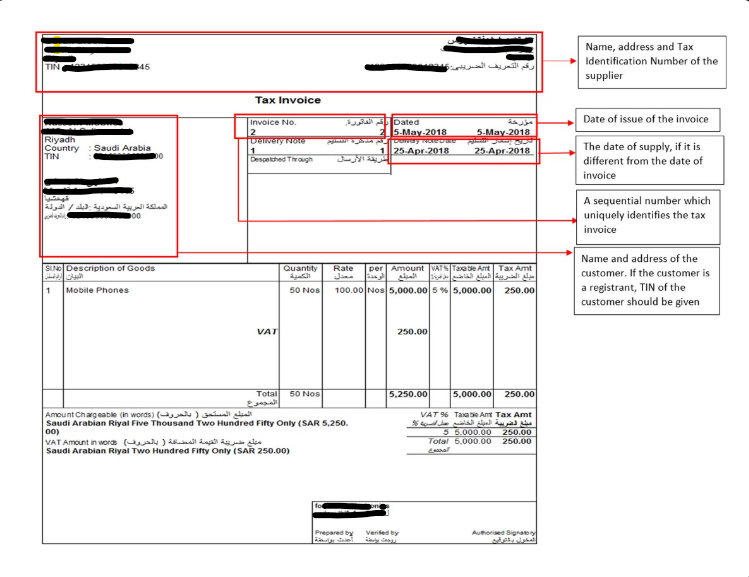
A sample VAT invoice format
Case-Specific Details to Be Specified in a Tax Invoice
A tax invoice must include specific details based on the nature of the transaction. Below are the case-specific elements that should be clearly stated:
1. Date of Supply (if different from the Invoice Date)
If the actual date of supply differs from the date on which the tax invoice is issued, the invoice must explicitly mention the supply date.
This ensures clarity in cases where goods or services are delivered on a different day than when the invoice is generated.
2. Explanation of Tax Treatment (If Tax is Not Applied at the Standard Rate)
If the applicable tax rate is different from the standard rate (e.g., reduced rate, zero rate, or exemption), the invoice must include a narrative description explaining the tax treatment.
This explanation helps both the supplier and the customer understand why the standard tax rate was not applied and ensures compliance with tax regulations.
3. Self-Accounting for Tax by the Customer (Reverse Charge Mechanism)
In certain cases, the responsibility for accounting for tax may shift from the supplier to the customer. When this occurs, the tax invoice must include the following details:
- The Tax Identification Number (TIN) of the customer.
- A clear statement indicating that the customer is required to account for the tax under the reverse charge mechanism.
This requirement is particularly relevant in cross-border transactions or cases where specific tax laws mandate that the buyer self-assesses and remits the tax instead of the seller.
4. VAT on the Sale of Used Goods (Margin Scheme)
When the supply involves used goods and VAT is applied under a margin scheme, the invoice must comply with the following conditions:
- It should explicitly state that VAT is charged only on the profit margin rather than on the full selling price.
- The invoice must not display the VAT amount separately to align with tax regulations governing margin schemes.
This approach ensures that VAT is correctly calculated and reported, preventing any misunderstanding regarding tax liability.
VAT registrants must issue fully and VAT compliant tax invoices, specifying all necessary information under VAT law. Suppliers must also issue valid tax invoices, ensuring they are present in purchases. This template can help businesses design automated invoicing systems for VAT compliant invoices, reducing manual effort.
On Nov 1, 2024, ZATCA announced that wave 17 of phase 2 covers those entities registered under KSA VAT, whose 2022 or 2023 turnover is more than SAR 2.5 million. Hence relevant companies shall link their ERP/POS by July 31, 2025.
Common mistakes to avoid
Businesses regularly face numerous errors while making prepared VAT invoices. Compliance can lead to monetary results because of the ones errors. This list will provide some of the most common mistakes, which might be avoided with the aid of following such commands:
- Incorrect Information: Either lacking or incorrect facts relating to the vendor's or customer's names, addresses, or VAT registration variety.
- Omitting Mandatory Components: Lack of bill variety, date, or supply date.
- Incorrect VAT Rate: The application of a wrong VAT price (e.g., using the same vintage price in place of zero-rated for sure gadgets).
- Calculation Errors: Calculation mistakes on well-known portions, VAT amounts, or line object totals.
- Invalid or Missing VAT Numbers: Providing an invalid VAT amount or not imparting it in any respect.
- Incorrect Payment Information: Giving incorrect monetary institution account facts or fee commands.
- Failure to Include a Billing Reference for Credit/Debit Notes: Failure to embody a connection with the actual bill while issuing credit score or debit notes.
- Poor Record Keeping: Failure to keep right records of issued invoices can motive problems at some stage in audits.
- Failure to Comply with ZATCA Regulations: Failure to conform with unique necessities stipulated with the aid of ZATCA, which includes e-invoicing protocols.
- Use of Manual Systems: The use of paper invoices results in delays and errors because of human oversight.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Format of a Tax Invoice in Saudi Arabia?
The e-invoice format in Saudi Arabia follows the guidelines set by the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA). A tax invoice must include specific details to ensure compliance with e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia regulations.
Key Elements of a Tax Invoice:
Title: The invoice must be labeled as a "Tax Invoice."
Supplier Details: Business name, VAT registration number, and address.
Customer Details: Name, VAT number (if applicable), and address.
Invoice Date & Time: The date and time when the invoice is issued.
Unique Invoice Number: A sequential number for tracking.
Description of Goods/Services: Quantity, unit price, and total value.
VAT Details: Tax rate, VAT amount, and total invoice amount (including VAT).
QR Code (for e-invoices): Required for simplified tax invoices under ZATCA e-invoice regulations.
Supply Date (if different from invoice date): Must be mentioned separately.
Total Amount Payable: Including VAT and any applicable discounts.
Types of E-Invoices in Saudi Arabia:
Standard Tax Invoice: Used for B2B transactions and must include a QR code and cryptographic stamp.
Simplified Tax Invoice: Used for B2C transactions with a mandatory QR code.
Saudi Arabia mandates the use of structured formats such as XML or PDF/A-3 with embedded XML for e-invoices.
What is the Format of a VAT Number in Saudi Arabia?
In Saudi Arabia, the VAT number format is a 15-digit numerical code issued by ZATCA to registered businesses for tax identification purposes.
Structure of the VAT Number:
Example VAT Number: 3XX-XXXXXX-XXXXXX
First Digit (3): Indicates the country code for Saudi Arabia.
Next 8 Digits: Unique identifier assigned to the taxpayer.
Next 4 Digits: A security key used for validation.
Last 2 Digits: Check digits for verification.
How to Verify a VAT Number?
Businesses can verify the validity of a VAT number through the ZATCA VAT verification portal to ensure compliance with Saudi tax regulations.
What are the Requirements for an Invoice in Saudi Arabia?
To comply with e-invoicing in Saudi Arabia, invoices must meet ZATCA’s regulations, including mandatory fields, digital format, and real-time reporting.
Key Requirements for an Invoice in Saudi Arabia:
Supplier’s and buyer’s name, VAT number, and address.
Invoice issue date and unique invoice number.
Description of goods/services, unit price, quantity, and total amount.
VAT rate and amount applied to each item.
Archiving and Reporting:
Invoices must be stored digitally for at least 6 years.
Large businesses must report invoices in real time through ZATCA’s system.
By following these e-invoice format requirements, businesses ensure compliance with Saudi Arabia’s VAT regulations and avoid penalties.
Explore more Products









