- What is MIS?
- What is the need for MIS?
- Components of MIS
- Types of information system
- Types of MIS reports in TallyPrime
Organisations today use data-driven strategies to lead their business. They generate reports to measure their achievements and design future directions for every business area. Management Information System (MIS) reports help organisations succeed in maintaining and managing the pieces of information gathered to generate reports for further analysis and business improvement.
In this detailed guide, we will discuss the meaning, purpose, and types of MIS reports available while also focusing on how these reports are created, what industries use MIS reports, what challenges your businesses face when using MIS reports, and how TallyPrime can enhance these reports.
What is MIS?
A Management Information System (MIS) report in accounting is a structured document that converts raw business data into meaningful insights. These reports help business owners and managers track performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions. Essentially, an MIS report acts as a decision-support tool, enabling leaders to measure achievements, allocate resources efficiently, and plan for future growth.
In accounting, MIS reports bring together financial and operational data to give a clear snapshot of how the business is performing. For instance, a company can generate reports to monitor cash flow, profitability, sales, or productivity, helping management stay proactive rather than reactive.
Why MIS Reports Matter for Decision-Making
In today’s competitive environment, data-driven decision-making is crucial for sustainable business growth. MIS reports simplify large data sets into actionable insights that:
- Highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) across departments
- Identify areas of cost leakage or inefficiency
- Improve forecasting and budgeting accuracy
- Help businesses comply with financial and regulatory requirements
Whether it’s a small retail store tracking daily sales or a manufacturing company analyzing production efficiency, MIS reports ensure that decision-makers always have real-time, accurate information at their fingertips.
Who Benefits from MIS Reports?
MIS reports are essential across all business sizes and industries, including:
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): For cash flow tracking, expense management, and performance evaluation
- Large Enterprises: For multi-department analysis, consolidated reporting, and compliance tracking
- Retail Sector: To monitor sales performance, customer preferences, and stock movement
- Manufacturing: For production planning, supply chain optimization, and cost control
- Healthcare: For financial management, billing efficiency, and service quality tracking
- Finance and Banking: To ensure regulatory compliance, assess profitability, and improve decision-making accuracy
By providing accurate, structured, and visual information, MIS reports act as the foundation of data-backed management in every industry.
What is the need for MIS?
The following are some of the justifications for having an MIS system
- Decision makers need information to make effective decisions. Management Information Systems (MIS) make this possible.
- MIS systems facilitate communication within and outside the organization – employees within the organization are able to easily access the required information for the day to day operations. Facilitates such as Short Message Service (SMS) & Email make it possible to communicate with customers and suppliers from within the MIS system that an organization is using.
- Record keeping – management information systems record all business transactions of an organization and provide a reference point for the transactions.
Components of MIS
The major components of a typical management information system are;
- People – people who use the information system
- Data – the data that the information system records
- Business Procedures – procedures put in place on how to record, store and analyze data
- Hardware – these include servers, workstations, networking equipment, printers, etc.
- Software – these are programs used to handle the data. These include programs such as spreadsheet programs, database software, etc.
Types of information system
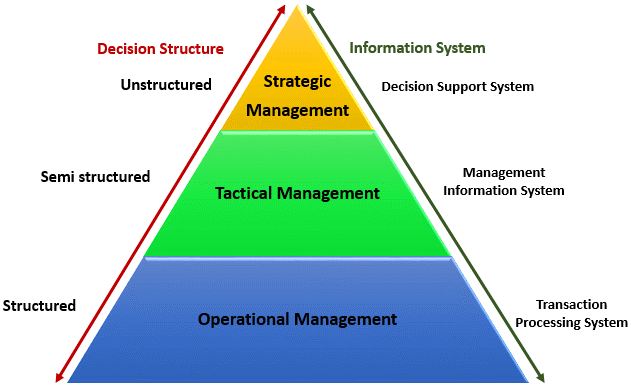
Management information systems find their way into just about every aspect of a company. They work with the people in the company, the technology in the company, its products, and the inter-relationships between all of these on a day-to-day basis. If you implement an MIS in your company, then the levels of efficiency you could potentially achieve with it are mind boggling.
Types of MIS reports
MIS reports can be categorised based on business functions. The most commonly used types are:
1. Financial reports
Financial MIS reports help gain an in-depth view of a company’s financial health and are needed for budgeting, forecasting, and investment planning. Some of the examples include:
Profit & loss statement – Summarises revenue, expenses, and net profit
Balance sheet – Gives the company’s snapshot of assets, liabilities and equity
Cash flow report – Records cash flows to ascertain liquidity and solvency
2. Operational reports
Operational reports help organisations monitor business processes, supply chain performance, and production efficiency. Such reports include:
Stock status and turnover – Checks on the prevailing stock levels and the inventory turnover rate.
Production reports – Tracks manufacturing output and efficiency
Supply chain reports – Analyses supplier/procurement and vendor performance
3. Sales and marketing reports
The sales and marketing divisions generate these reports to deliver information about customer actions, revenue creation patterns, and campaign performance metrics. The examples include:
Sales performance report – Analyses sales trends across different periods
Customer demographics report – Evaluates customer buying patterns and preferences
Marketing ROI report – Assesses the success of marketing campaigns
4. HR reports
The organisation depends strongly on HR MIS Reports to track various aspects of workforce management, employee performance zones, and HR policy enhancements. Such reports include:
Employee productivity report – Measures individual and team efficiency
Payroll & compensation report – Tracks salaries, bonuses, and deductions
Training & development reports - Monitors programs that improve employee competencies
Each report contributes strongly to business management activities by supporting data-centered decision-making.
5.Management Control Report
MIS Report Comparison Table
| Report Name | Key Insights | Best For | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Report | Profitability, revenue, expenses | Finance teams, auditors | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Operational Report | Stock, supply chain, production | Operations, manufacturing | Daily/Weekly |
| Sales & Marketing Report | Sales performance, ROI, customer insights | Sales/Marketing teams | Weekly/Monthly |
| HR Report | Workforce performance, payroll, training | HR managers | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Management Control Report | Budgeting, forecasting, cost control | Senior management | Quarterly/Annually |
How to create an MIS report? (Step-by-step guide)
MIS reports can be generated manually or using accounting/ERP software like TallyPrime.
Manual process
The preparation of manual MIS needs a structured methodology. The steps include:
- Describing the report targets by determining its primary function, whether for financial monitoring or sales evaluation.
- Obtaining data by working with several departments, including finance, sales and operations.
- Achieving accurate analysis of raw data to execute data cleaning steps for structure and organisation.
- Identifying patterns together with trends and anomalies in the analysis phase.
- Incorporating visual representation systems based on tables, graphs, and charts in the preparation phase.
- Reviewing and conducting validating checks to ensure accuracy in the findings for stakeholder presentation.
Using accounting/ERP software
Using software solutions to generate MIS reports makes the process smoother, ensuring utmost accuracy. TallyPrime, when used, streamlines operations following the below-mentioned steps..
- Enter financial, sales, or operational data into TallyPrime.
- Choose from pre-defined templates for reports.
- Use the Customise Report screen to execute data filtering features based on time, location, and other parameters.
- Transform data into PDF, Excel, and alternative output configurations through the Generate & Export feature.
The report generated using TallyPrime is accurate and delivers real-time information to users.
Why do industries need MIS reports?
MIS helps to improve decision-making, increases operational efficiency, and strengthens an organization’s competitive position. MIS provides accurate, timely data and analytical tools so managers can understand what is happening, identify what needs attention, and plan what should happen next. By connecting departments and providing a single source of truth, MIS ensures that everyone works with consistent information, leading to better coordination and stronger results.
Key reasons industries need MIS:
1. Improved decision-making
MIS provides managers with real-time, accurate data and built-in analysis tools. This helps organizations detect problems early, identify new opportunities and make fast, data-driven decisions.
2. Enhanced efficiency
MIS automates routine tasks and workflows. As a result, it will help manual effort decreases, human errors reduce, employees can focus on strategic and high-value work.
3. Stronger strategic planning
With historical data and forecasting capabilities, MIS enables businesses to identify performance trends, anticipate market changes, build effective long-term strategies.
4. Better coordination and communication
A central, shared database helps integrate departments. This leads to smoother information flow, better collaboration, stronger overall coordination across the organization.
5. Competitive advantage
MIS helps businesses respond quickly to market conditions by optimizing processes, improving decision speed, boosting operational performance. This can help organizations outperform competitors.
6. Performance tracking and control
MIS maintains accurate records of business transactions, employee performance, operational and financial activities. This gives leadership greater visibility and control.
7. Improved resource optimization
MIS provides clarity on how resources are being used. This helps organizations allocate financial, human and material resources more effectively and reduce waste.
Industry-specific applications of MIS reports
MIS reports are crucial for business operations in the following sectors:
1. Retail
Numerous retail businesses use these reports to analyse customer behaviours alongside inventory management and sales projection applications. For example, a supermarket chain enters data to generate inventory reports for stock monitoring and overstock prevention.
2. Manufacturing
MIS reports serve as production efficiency and supply chain operation monitoring tools for manufacturers. A factory monitoring manufacturing output using production reports to detect operational problems is an example here.
3. Healthcare
Using these reports enables healthcare institutions and hospitals to manage their patient records alongside optimising operational processes and handling their billing procedures. A healthcare institution uses financial MIS reports to track medical service revenue alongside insurance claim information.
Types of MIS reports in TallyPrime
- Accounting reports
To obtain information on the financial position, operational performance and economic activities of the business.
- Financial reports
To determine the financial condition of an organisation as required by shareholders, creditors and government units.
- Inventory reports
To manage the Inventory effectively since the actual status of stock items is obtained.
- Management control reports
To utilise budgets, cost centre reports, scenario reports etc. for controlling activities.
Wish to make your business more efficient and processes more streamlined? Give TallyPrime a shot and we promise you will not be disappointed.
FAQs
1. What are the key components of an effective MIS report?
An effective MIS report includes:
- Clear objectives – What the report aims to explain or monitor
- Accurate and relevant data – Only information that supports decision-making
- KPIs and metrics – Quantifiable indicators of performance
- Comparisons and trends – Month-over-month or year-over-year views
- Visual summaries – Charts, graphs, dashboards, or tables
- Insights and interpretation – What the numbers mean for the business
- Action recommendations – Steps to improve performance or resolve issues
A good MIS report is concise, structured, and directly supports business decisions.
2. How often should MIS reports be generated?
The frequency depends on business needs and the type of data. Typically:
- Daily: Sales, cash flow, inventory status, attendance
- Weekly: Production reports, expense monitoring, operational updates
- Monthly: Financial performance, profitability, budgeting, management reviews
- Quarterly: Strategic performance, forecasting, compliance reviews
The goal is to generate MIS reports frequently enough to keep decision-makers informed without overwhelming them.
3. Can MIS reports be automated?
Yes. Most MIS reports today can and should be automated. Automation helps by pulling real-time data from various departments, reducing manual data entry errors, saving time for managers and ensuring timely and consistent reporting.
Tools like TallyPrime, BI dashboards, and spreadsheet automations make MIS reporting largely auto generated.
4. What software tools can I use to create MIS reports?
You can create MIS reports using:
- TallyPrime – For financial, accounting, inventory, and operational MIS
- Excel / Google Sheets – Flexible templates, charts, formulas
- Business Intelligence (BI) tools – Power BI, Tableau, Zoho Analytics
- ERP systems – For integrated and automated reporting
- Custom dashboards – For real-time insights and KPI tracking
The best tool depends on your organization's size, data complexity, and reporting needs.
5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating an MIS report?
Avoid these mistakes:
- Including too much data (information overload)
- Lack of clarity in objectives or definitions
- Using outdated or inaccurate data
- Poor formatting that makes insights hard to spot
- No actionable recommendations
- Complex language or jargon that confuses readers
- Not aligning the report with key business goals
- A good report focuses on insights, not just numbers.
6. How do I analyze the data in an MIS report?
To analyze MIS data effectively:
- Identify key metrics that relate to performance goals
- Look for patterns or trends (increase, decrease, stability)
- Compare data – month-to-month, year-to-year, or against targets
- Spot anomalies or discrepancies that need investigation
- Understand root causes of changes
- Assess business impact using financial or operational outcomes
- Create actionable recommendations based on the insights
The purpose of analysis is to move from raw numbers → meaningful insights → decisions.
7. What should I include in an MIS report for financial performance?
A financial MIS report should include:
- Revenue and sales performance
- Profit and loss analysis
- Cash flow summary
- Expenses and cost breakdown
- Budget vs. actual comparison
- Accounts receivable and payable status
- Key financial ratios (profit margin, liquidity, debt ratio, ROI)
- Variance analysis
These elements help management evaluate financial health and make budgeting decisions.
8. How do MIS reports help with decision-making?
MIS reports support decision-making by providing:
- Accurate real-time data needed to understand business performance
- Trend analysis that shows what is working and what isn’t
- Forecasts that help plan for the future
- KPIs and metrics that highlight priorities
- Early warning signals for issues like declining sales or rising costs
- Performance insights that guide operational and strategic decisions
In short, MIS reports turn data into insight, and insight into informed action.

















